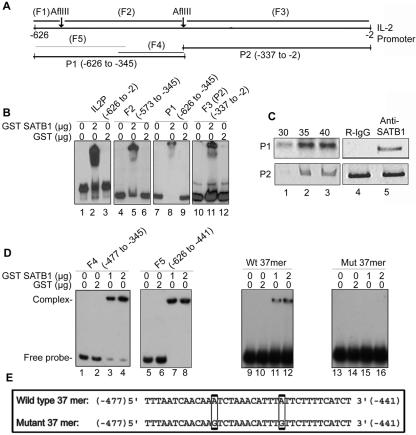
FIG. 2.
SATB1 binds to the human IL-2 promoter in vitro and in vivo. (A) Schematic representation of 0.62-kb IL-2 promoter sequence spanning base pair −626 to −2 region of translation start site. The positions of the probes used for EMSA and ChIP are as indicated. (B) SATB1 binds to the IL-2 promoter in vitro. Mapping of the binding site of SATB1 in the IL-2 promoter region (IL2P) was performed by EMSA analysis as described in Materials and Methods, using 2 μg of bacterially expressed and purified GST-SATB1 and 32P-labeled probes. An equal amount of GST was used as a control in binding reactions. The probes were generated using AflIII restriction digestion (F2 and F3) or PCR amplification using specific primer pairs (full length and P1). (C) In vivo binding of SATB1 to the distal IL-2 promoter. Anti-SATB1 immunoprecipitated chromatin from CEM-GFP cells was amplified with P1 (top) and P2 (bottom) primer sets for 30 (lane 1), 35 (lane 2), and 40 (lane 3) cycles. ChIP analysis was again performed using rabbit IgG (R-IgG, lane 4, upper panel) and anti-SATB1 (lane 5, upper panel) and subjected to 30 cycles of PCR amplification with the P1 primer set. Input (lanes 4 and 5, bottom panel) denotes amplification of the DNA in soluble chromatin prior to immunoprecipitation. (D) SATB1 binds to the 37-mer ATC context present in the distal promoter (P1 region) of the IL-2 promoter. The ATC context containing overlapping regions F4 (−477 to −345) and F5 (−626 to −441) were amplified by PCR using specific primers and labeled using [32P]dCTP. EMSA analysis was performed using 1 (lanes 3 and 7) or 2 (lanes 4 and 8) μg of GST-SATB1 or 2 μg of GST alone (lanes 2 and 5). Wild-type (Wt) and mutant (Mut) forward and reverse 37-mer oligonucleotides were annealed and end labeled with [32P]ATP. Wild-type annealed double-stranded 37-mer oligonucleotide (corresponding to nucleotides −477 to −441 of the IL-2 promoter) displays perfect ATC context whereas the mutant has two A-to-G changes that disrupt the ATC context. Binding reactions were performed as described for F4 and F5. (E) Nucleotide sequences of the wild-type and mutated 37-mer ATC context spanning the region from base pair −477 to base pair -441 from the translation start site of IL-2. The two mutated nucleotides are shown in boxes.