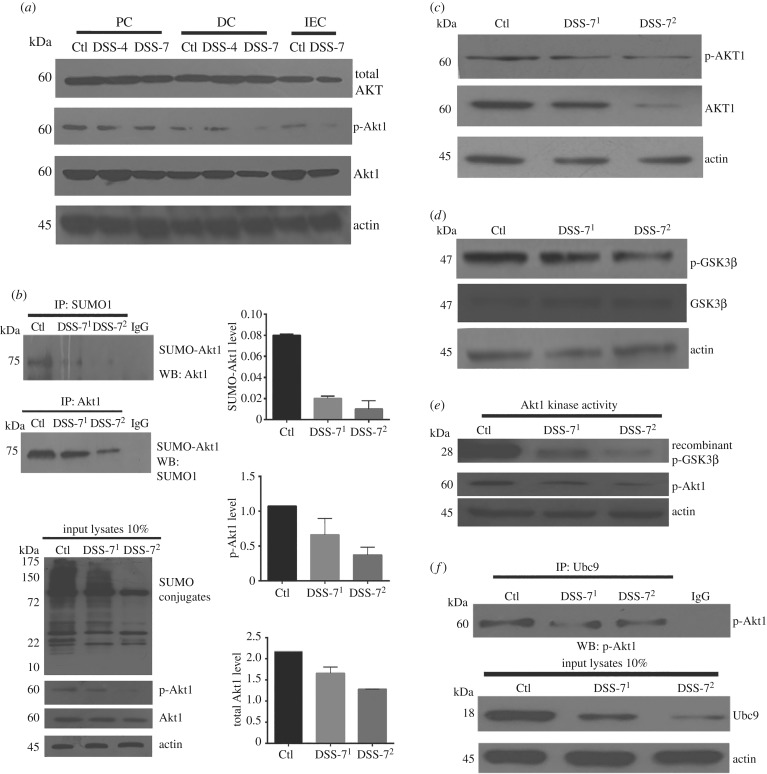
Figure 5.
DSS mice display lowered SUMOylated Akt1 and compromised kinase activity. (a) Immunoblots of total AKT, Akt1 and pAkt1 (S473) of proximal colon (PC), distal colon (DC) and colonic intestinal epithelium (IEC). (b) Various colonic tissue lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-SUMO1 antibodies (upper panel) and immunoblotted for Akt1 showing reduced SUMO Akt1 in DSS-treated mice and IP with anti-Akt1 antibody and probed for SUMO-1 to detect SUMOylated-Akt1. Ten per cent of the input was loaded as shown in the blot (bottom panel). The ratios of SUMO-Akt1/Akt1 as well as pAkt1/Akt1 are shown based on densitometric values obtained from the IP immunoblots. (c) Immunoblots of total Akt1 and phospho-Akt1 (S473) from colonic lysates of mice. (d) Immunoblot of phospho-GSK3β (S9) and total GSK3β from mice samples. (e) Colonic epithelial lysates from control and DSS-treated animals were added to Akt-specific kinase activity mixture involving recombinant GSK3β (28 kDa), ATP and optimal buffer for 30 min at 30°C. Akt kinase activity was then determined by immunoblotting for pGSK3β. (f) Ubc9 and Akt1 interaction was tested using IP of colonic lysates with anti-Ubc9 antibody and probed with anti-phospho-Akt1 antibody, input lysates are represented at the bottom. β-Actin was used as a loading control. In all IP experiments and kinase assays, an equal amount of total protein (500 µg) was used in each category of samples. Mice samples DSS-71 (Ubc9 < sixfold downregulation: Ubc9Low) and DSS-72 (Ubc9 > sixfold downregulation: Ubc9HyperLow) are compared with control mice samples.