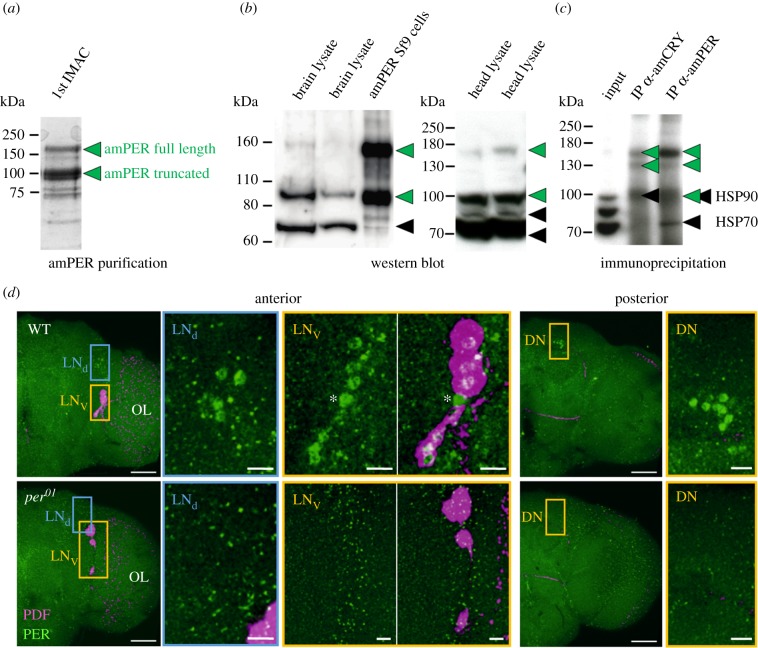
Figure 1.
Antibody production and validation. (a) Purification of recombinant amPER for rabbit immunization. Two species of amPER were apparent throughout the purification process. Displayed is a single fraction from the first step of amPER purification via IMAC separated on SDS-PAGE (Coomassie staining). (b) Validation of antibody in WBs. In bee tissue extracts, the amPER antibody detects up to four main bands (plus occasional laddering of top band), of which two correspond directly to the two species of recombinant amPER observed in Sf9 cells (green arrowheads, see also (a)). The other two bands likely result from unspecific binding (black arrowheads). (c) Validation of antibody using IP followed by mass spectrometry analysis. The amPER antibody enriches only amPER-specific signals (green arrowheads) in IP from bee head lysates but gives some unspecific signal in WBs (black arrowheads). Displayed is an anti-amPER WB of IPs with either amPER or amCRY antibody. (d) Validation of antibody in immunohistochemistry. Double staining with antibodies against amPER (green) and PDF (magenta) in wholemount brains of D. melanogaster wild-type (WT) and period null mutant (per01) flies. In the anterior right brain hemisphere of WT flies, the nuclei of the typical LNd and LNv cell clusters are stained with amPER. All cells of the LNv cluster, except one (asterisk), co-express PDF. In the posterior right brain hemisphere, the nuclei of the DNs are labelled. In per01 brains, none of the cell clusters was labelled by amPER, only unspecific staining (green dots) can be seen. OL, optic lobe. Scale bars in hemisphere views: 50 µm. Scale bars in magnified pictures: 10 µm. Pictures are taken with a 25× objective (0.6 numerical aperture); distance of z-stacks: 1 µm (six overlaid stacks in the anterior brain and 22 overlaid stacks in the posterior brain).