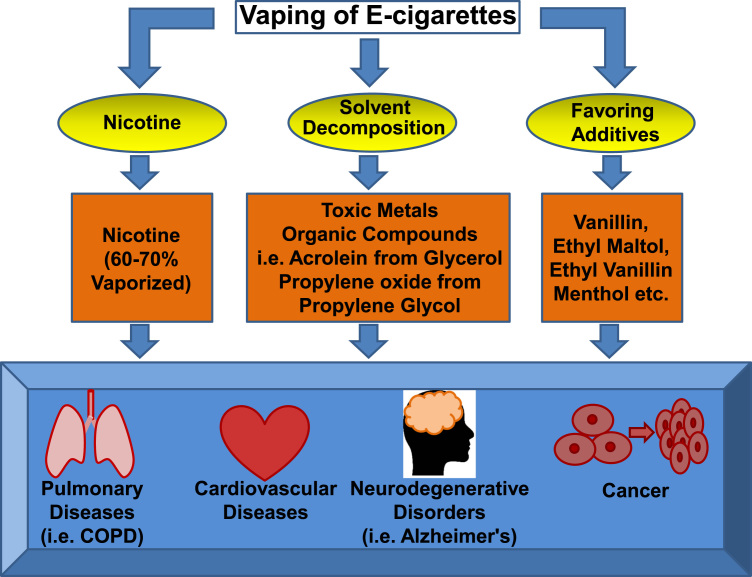
Fig. 2.
Pathological effects induced by e-cigarette components and vaporization products. Most of the e-cigarettes used for smoking cessation contain nicotine, which can be vaporized by 60–70%. Thermal decomposition of e-cigarette solvents results in release of toxic metals, and formation of an array of organic compounds such as acrolein from glycerol, and propylene oxide from propylene glycol. Frequently used flavoring additives include vanillin, ethyl matol, ethyl vanillin, and methol. All of these components and vaporization products have been shown to be either directly carcinogenic, or toxic in inducing cardiopulmonary diseases and neurodegenerative disorders.