Abstract
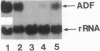
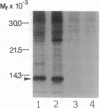
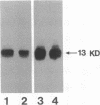
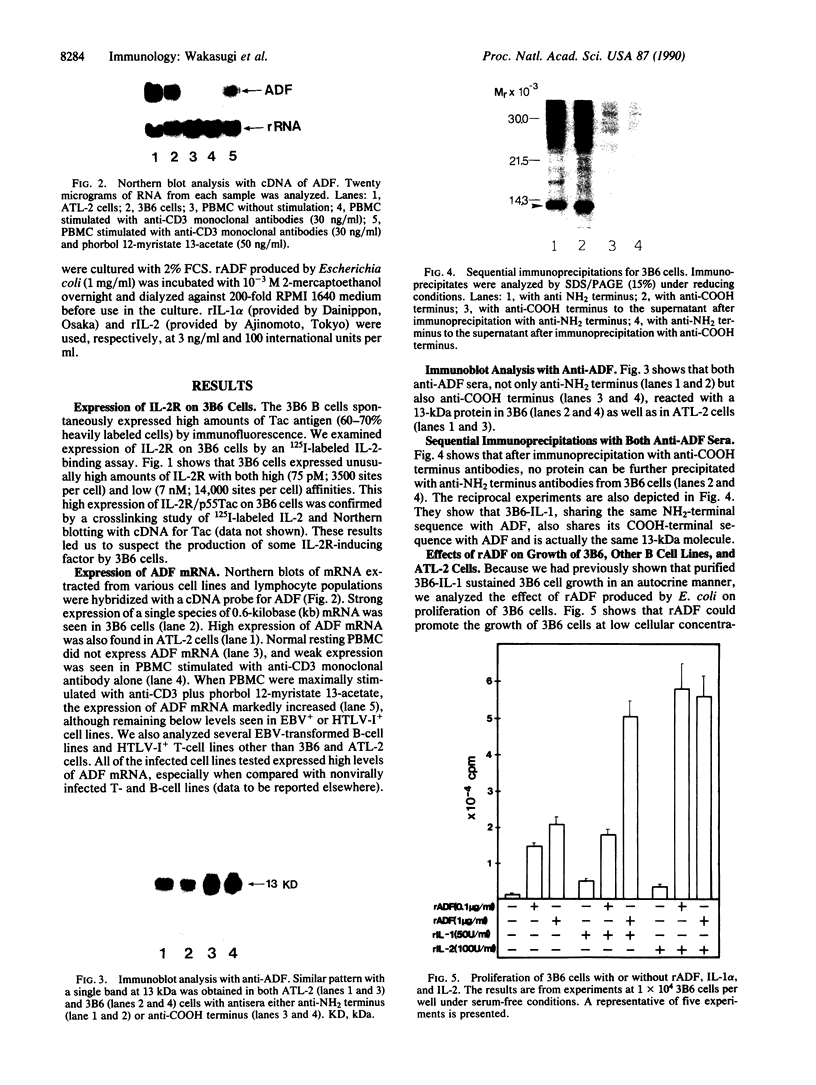
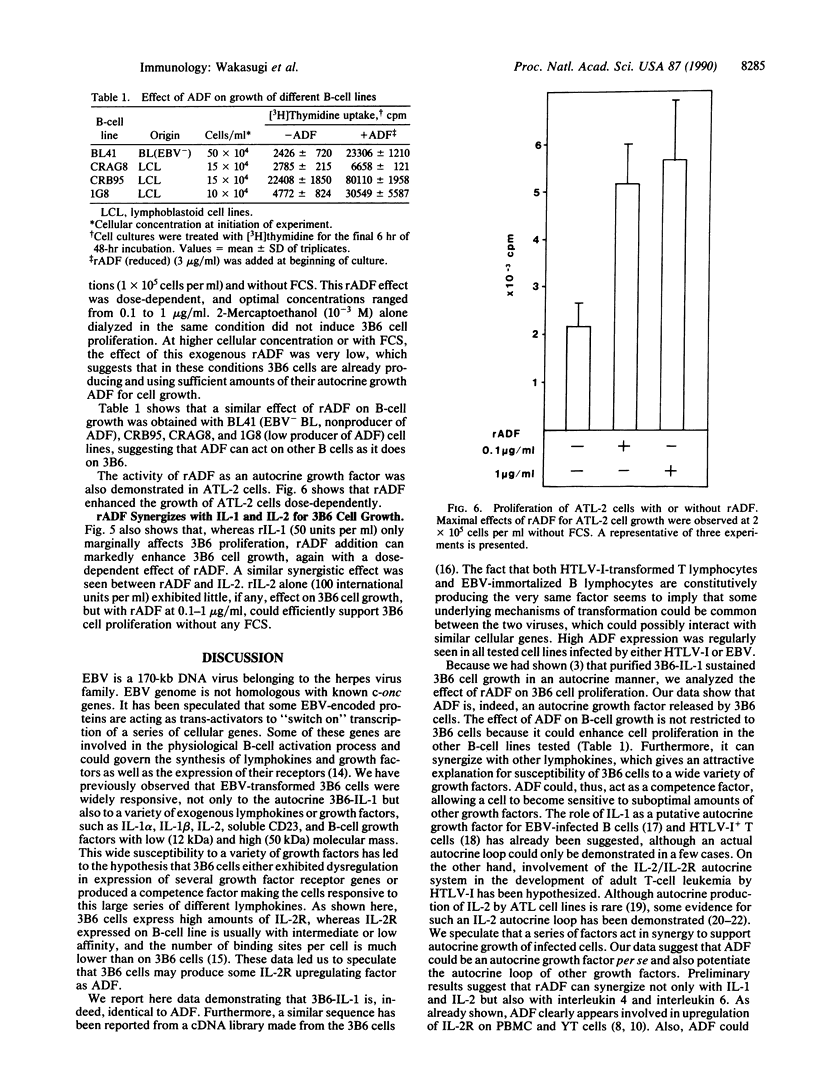
Interleukin 1 (IL-1) has been obtained from the Epstein-Barr virus-infected B-lymphoblastoid cell line 3B6 and shown to be involved in autocrine growth of 3B6 B cells. Independently, adult T-cell leukemia-derived factor (ADF) was purified from human T-lymphotropic virus I-infected leukemic T-cell line (ATL-2) and reported as an interleukin 2 (IL-2) receptor-inducing factor. We have previously reported the same molecular mass, pI, and NH2-terminal amino acid sequence for both 3B6-derived IL-1 and ADF. cDNA cloning of ADF demonstrated high homology with the prokaryotic disulfide reducing enzyme thioredoxin. We show here that ADF and 3B6-derived IL-1 are identical. By RNA blot, 3B6 and ATL-2 cells were shown to contain high levels of 0.6-kilobase mRNA corresponding to ADF. Such message was not detected in resting peripheral blood lymphocytes but could be weakly induced by lymphocyte activation. Antibodies have been raised against synthetic peptides corresponding to the NH2 terminus and the COOH terminus of ADF. Immunoblotting and sequential immunoprecipitation with these antibodies revealed the same 13-kDa protein in 3B6 and ATL-2 cells. Recombinant ADF could sustain growth of 3B6 and ATL-2 cells at low cellular concentration without fetal calf serum; ADF, thus, appears involved in their autocrine growth. Similarly, recombinant ADF could enhance growth of other B-cell lines, including the Epstein-Barr virus-negative Burkitt lymphoma line BL41 and the lymphoblastoid cell lines CRAG8, CRB95, and 1G8. Finally, recombinant ADF exhibits marked synergism with other cytokines, such as IL-1 and IL-2, allowing virally infected lymphocytes to respond to suboptimal amounts of a variety of growth factors.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arya S. K., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C. T-cell growth factor gene: lack of expression in human T-cell leukemia-lymphoma virus-infected cells. Science. 1984 Mar 9;223(4640):1086–1087. doi: 10.1126/science.6320374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett C. F., Balcarek J. M., Varrichio A., Crooke S. T. Molecular cloning and complete amino-acid sequence of form-I phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):268–270. doi: 10.1038/334268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensimon C., Wakasugi N., Tagaya Y., Takakura K., Yodoi J., Tursz T., Wakasugi H. Two distinct affinity binding sites for IL-1 on human cell lines. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1168–1174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Retroviruses as etiologic agents of some animal and human leukemias and lymphomas and as tools for elucidating the molecular mechanism of leukemogenesis. Blood. 1982 Sep;60(3):545–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman M. G., Weigle W. O. Nonspecific activation of murine lymphocytes. V. Role of cellular collaboration between T and B lymphocytes in the proliferative and polyclonal response to 2-mercaptoethanol. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1433–1439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grippo J. F., Tienrungroj W., Dahmer M. K., Housley P. R., Pratt W. B. Evidence that the endogenous heat-stable glucocorticoid receptor-activating factor is thioredoxin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13658–13664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren A. Reduction of disulfides by thioredoxin. Exceptional reactivity of insulin and suggested functions of thioredoxin in mechanism of hormone action. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9113–9119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren A. Thioredoxin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:237–271. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda M., Arima N., Daitoku Y., Kashihara M., Okamoto H., Uchiyama T., Shirono K., Matsuoka M., Hattori T., Takatsuki K. Evidence for the interleukin-2 dependent expansion of leukemic cells in adult T cell leukemia. Blood. 1987 Nov;70(5):1407–1411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda M., Shimizu A., Ikuta K., Okamoto H., Kashihara M., Uchiyama T., Honjo T., Yodoi J. Origin of human T-lymphotrophic virus I-positive T cell lines in adult T cell leukemia. Analysis of T cell receptor gene rearrangement. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):2169–2174. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.2169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mark D. F., Richardson C. C. Escherichia coli thioredoxin: a subunit of bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):780–784. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama M., Shibuya H., Harada H., Hatakeyama M., Seiki M., Fujita T., Inoue J., Yoshida M., Taniguchi T. Evidence for aberrant activation of the interleukin-2 autocrine loop by HTLV-1-encoded p40x and T3/Ti complex triggering. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):343–350. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90437-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimsky L., Wakasugi H., Ferrara P., Robin P., Capdevielle J., Tursz T., Fradelizi D., Bertoglio J. Purification to homogeneity and NH2-terminal amino acid sequence of a novel interleukin 1 species derived from a human B cell line. J Immunol. 1986 May 1;136(9):3304–3310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scala G., Kuang Y. D., Hall R. E., Muchmore A. V., Oppenheim J. J. Accessory cell function of human B cells. I. Production of both interleukin 1-like activity and an interleukin 1 inhibitory factor by an EBV-transformed human B cell line. J Exp Med. 1984 Jun 1;159(6):1637–1652. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.6.1637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidman C. L., Unanue E. R. Control of proliferation and differentiation in B lymphocytes by anti-Ig antibodies and a serum-derived cofactor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2401–2405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagaya Y., Maeda Y., Mitsui A., Kondo N., Matsui H., Hamuro J., Brown N., Arai K., Yokota T., Wakasugi H. ATL-derived factor (ADF), an IL-2 receptor/Tac inducer homologous to thioredoxin; possible involvement of dithiol-reduction in the IL-2 receptor induction. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):757–764. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03436.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagaya Y., Okada M., Sugie K., Kasahara T., Kondo N., Hamuro J., Matsushima K., Dinarello C. A., Yodoi J. IL-2 receptor(p55)/Tac-inducing factor. Purification and characterization of adult T cell leukemia-derived factor. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 15;140(8):2614–2620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teshigawara K., Maeda M., Nishino K., Nikaido T., Uchiyama T., Tsudo M., Wano Y., Yodoi J. Adult T leukemia cells produce a lymphokine that augments interleukin 2 receptor expression. J Mol Cell Immunol. 1985;2(1):17–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley-Lawson D. A., Mann K. P. Early events in Epstein-Barr virus infection provide a model for B cell activation. J Exp Med. 1985 Jul 1;162(1):45–59. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchiyama T., Broder S., Waldmann T. A. A monoclonal antibody (anti-Tac) reactive with activated and functionally mature human T cells. I. Production of anti-Tac monoclonal antibody and distribution of Tac (+) cells. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1393–1397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakasugi H., Dokhelar M. C., Garson D., Harel-Bellan A., Fradelizi D., Tursz T. Accessory function of human leukemic cell lines: properties of B and B-K562 hybrid cell lines. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Mar;15(3):256–261. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakasugi H., Rimsky L., Mahe Y., Kamel A. M., Fradelizi D., Tursz T., Bertoglio J. Epstein-Barr virus-containing B-cell line produces an interleukin 1 that it uses as a growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):804–808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Goldman C. K., Robb R. J., Depper J. M., Leonard W. J., Sharrow S. O., Bongiovanni K. F., Korsmeyer S. J., Greene W. C. Expression of interleukin 2 receptors on activated human B cells. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1450–1466. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wano Y., Hattori T., Matsuoka M., Takatsuki K., Chua A. O., Gubler U., Greene W. C. Interleukin 1 gene expression in adult T cell leukemia. J Clin Invest. 1987 Sep;80(3):911–916. doi: 10.1172/JCI113152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollman E. E., d'Auriol L., Rimsky L., Shaw A., Jacquot J. P., Wingfield P., Graber P., Dessarps F., Robin P., Galibert F. Cloning and expression of a cDNA for human thioredoxin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15506–15512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yodoi J., Takatsuki K., Masuda T. Letter: Two cases of T-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia in Japan. N Engl J Med. 1974 Mar 7;290(10):572–573. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197403072901018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yodoi J., Teshigawara K., Nikaido T., Fukui K., Noma T., Honjo T., Takigawa M., Sasaki M., Minato N., Tsudo M. TCGF (IL 2)-receptor inducing factor(s). I. Regulation of IL 2 receptor on a natural killer-like cell line (YT cells). J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1623–1630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yodoi J., Uchiyama T. IL-2 receptor dysfunction and adult T-cell leukemia. Immunol Rev. 1986 Aug;92:135–156. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01498.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]