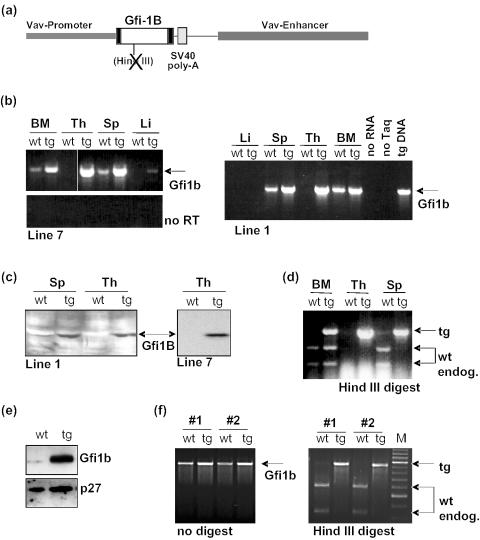
Figure 1.
Generation and analysis of vav-Gfi1b transgenic mice. (a) Schematic representation of the vav-Gfi1b construct used to generate transgenic mice. The Gfi1b cDNA was placed under the control of the enhancer and promoter elements of the vav gene. To terminate transcription, a SV 40 polyadenylation signal was inserted at the end of the Gfi1b cDNA. (b) Expression of the vav-Gfi1b transgene was detected by RT–PCR in bone marrow (BM), spleen (Sp) and thymus (Th) of two mouse lines (1 and 7). In both the lines, higher levels of mRNA were apparent in all the three organs of vav-Gfi1b transgenic mice (tg) than in wild-type animals (wt). Endogenous Gfi1b mRNA was present in bone marrow and spleen of wt mice but was absent in thymus and liver (Li) from wt mice. The signal in the transgenic liver from line 7 is very probably due to the contamination with blood cells. (c) Significantly higher levels of Gfi1b protein were detected by immunoblot in extracts from spleen (Sp) and thymus (Th) from vav-Gfi1b transgenic mice (tg) than from wild-type animals (wt). (d) HindIII digestion of RT–PCR products distinguishes between endogenous (wt) and transgenic Gfi1b expression. Endogenous Gfi1b expression is lost in spleen but not in bone marrow of vav-Gfi1b transgenic mice. (e) Detection of Gfi1b protein expression levels by immunoblot in cell lines established after infection of bone marrow from wt or vav-Gfi1b transgenic mice (tg) with a pSRα vector driving the expression of the p210 BCR/Abl fusion protein. Levels of p27 were analyzed to ensure uniform loading of the gel. (f) Expression of the wt and transgene Gfi1b-alleles was detected by RT–PCR in two independent BCR/Abl transformed B-cell lines (1 and 2) before and after HindIII digestion. Endogenous Gfi1b mRNA can be detected in both cell lines derived from wt bone marrow but is absent in the cell lines established from bone marrow of vav-Gfi1b transgenic mice.