Figure 1.
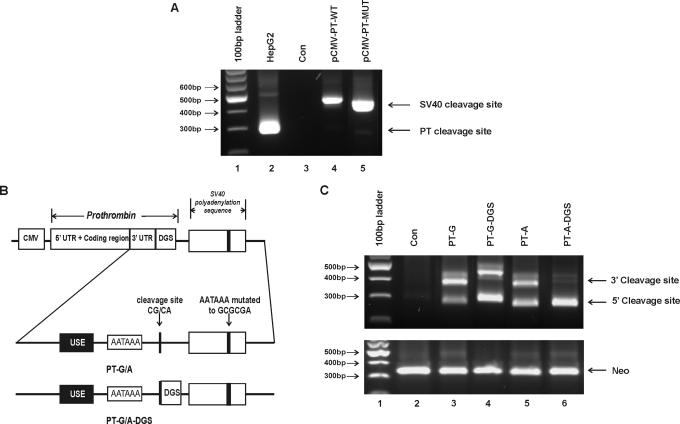
Prothrombin mRNA is cleaved and polyadenylated in the absence of DGS. (A) 3′RACE results of RNA isolated from cells stably transfected with prothrombin allelic variants. Lane 1, 100 bp DNA ladder; lane 2, Endogenous prothrombin mRNA detected in HepG2 cells; lane 3, HEK-293 cells transfected with the pCI-Neo vector (con); lanes 4 and 5, HEK-293 cells expressing wild-type (pCMV-PT-WT) or mutant (pCMV-PT-MUT) prothrombin variants, respectively, using the SV40 polyadenylation signal. (B) Schematic representation of the constructs expressing prothrombin variants. All constructs express the full-length prothrombin cDNA including the entire 3′-untranslated region (3′-UTR) under the control of the CMV promoter. Cleavage and polyadenylation elements involved in prothrombin 3′-end formation are indicated: USE, upstream sequence element; DGS, 50 bp downstream genomic sequence; AAUAAA, polyadenylation signal; CG/CA, polymorphic cleavage site. All constructs contain mutations within the SV40 polyadenylation signal (AAUAAA mutated to GCGCGA): PT-G/A, allelic prothrombin cDNA with no DGS; PT-G/A-DGS, prothrombin variant cDNA with 50 bp of DGS. (C) 3′RACE results of RNA isolated from HEK-293 cells transiently transfected with prothrombin allelic variants containing mutations within the SV40 poly A signal, with or without the DGS of prothrombin. Lane 1, 100 bp DNA ladder; lane 2, HEK-293 cells transfected with the pCI-Neo vector (con), lane 3, PT-G; lane 4, PT-G-DGS; lane 5, PT-A and lane 6, PT-A-DGS. The 5′ cleavage site represents mRNA produced using the natural prothrombin cleavage site. The slower migrating band (3′ cleavage site) depicts the cryptic downstream cleavage site within the vector sequence. Neomycin phosphotransferase (Neo) mRNA was used as a measure of transfection efficiency (lower panel).