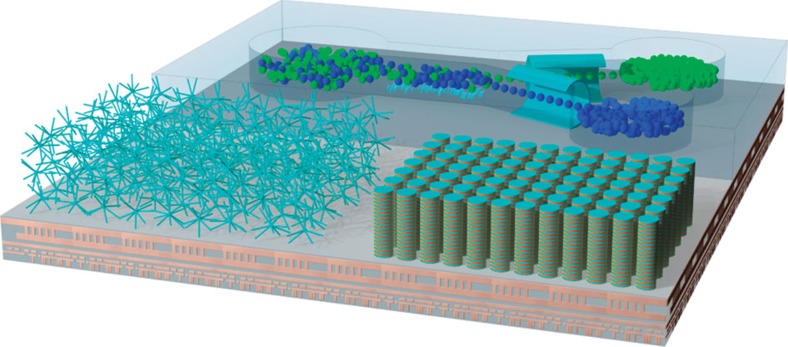
Figure 4. Futuristic vision of an Internet-of-Things chip integrating 3D magnetic nanostructures.
The chip is comprised of a microfluidic channel with two types of magnetic nanoparticles flowing from a common reservoir. The motion of fluid is achieved by magnetic NWs acting as artificial cilia. After particle separation by chemical means, individual particles entering each channel are detected via a nanomembrane magnetic flexible sensor. An array of vertical soliton conduits acts as an ultra-high-density 3D storage device, with read/write operations taking place on the substrate. Neuromorphic computing processes are carried out by a dense array of interconnected NWs.