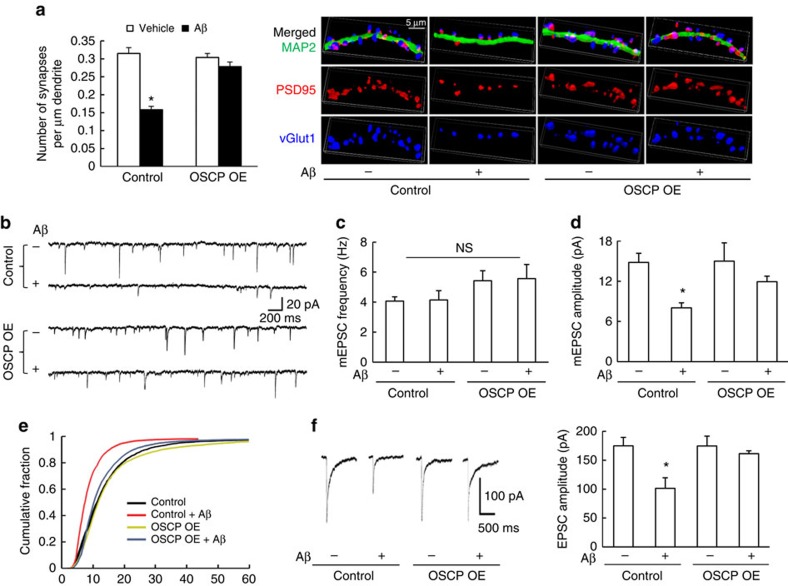
Figure 7. OSCP overexpression protects mouse neurons against Aβ induced synaptic dysfunction.
(a) Attenuated Aβ-induced synaptic density reduction in OSCP OE neurons. *P<0.01 versus other groups. n=26–43 neurons collected from at least three independent experiments. Synapses were visualized by the staining for vGlut1 (Blue) and PSD95 (red) to identify the pre- and postsynaptic components of synapses, respectively. Neuronal dendrites were determined by MAP2 (green). Scale bar, 5 μm. (b–e) OSCP overexpression protected mEPSCs from Aβ toxicity. (b) Representative traces of mEPSC recordings from control and OSCP OE neurons in the presence or absence of Aβ. Scale bars represent 200 ms and 20 pA. The data were collected from 10 vehicle-treated control neurons, 8 Aβ-treated control neurons, 7 vehicle-treated OSCP OE neurons and 8 Aβ-treated OSCP OE neurons. (c) Quantitative analysis of mEPSC frequency. (d) Quantitative analysis of mEPSC amplitude. *P<0.05 versus other groups. (e) The cumulative fraction of mEPSC amplitude distribution. (f) Overexpression of OSCP prevented the reduction in amplitude of glutamate-evoked EPSCs that results from Aβ toxicity in control neurons. Scale bars represent 500 ms and 100 pA. Data were collected from seven vehicle-treated control neurons, nine Aβ-treated control neurons, five vehicle-treated OSCP OE neurons and seven Aβ-treated OSCP OE neurons. Error bars represent s.e.m.