Figure 1.
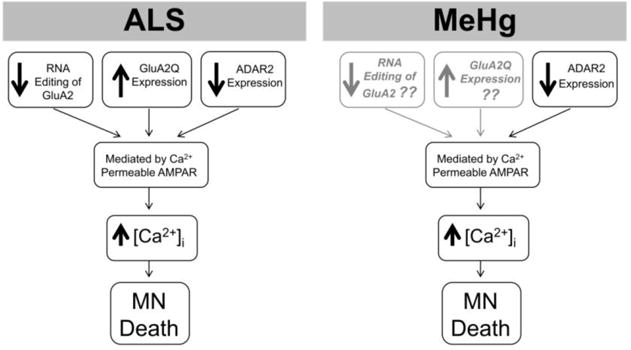
Role of AMPA receptors in ALS and MeHg toxicity on MNs. In ALS, AMPA receptors contribute to the alterations in intracellular Ca2+. This effect is in part due to the decrease in RNA editing of the GluA2, which results from a decrease in ADAR2. That contributes the increase in the unedited form of GluA2 (GluA2Q) containing receptors in MNs. This is one of the mechanisms that contribute to MN cell death in ALS. MeHg-induced Ca2+ dysregulation in MNs is also mediated in part by Ca2+ permeable AMPA receptors. Our preliminary studies have shown that there is a decrease of ADAR2. However, we do not know how and if the GluA2 subunit is affected by MeHg exposure. This should be the focus of future studies.
