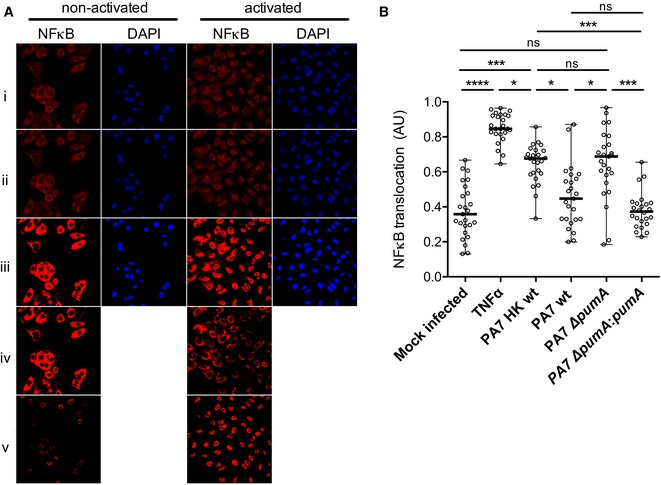
Control experiment in which A549 cells were either mock infected, treated with TNFα (1 μg/ml) or infected with either heat‐killed (HK)
P. aeruginosa PA7, wt, ∆
pumA, ∆
pumA::pumA (Ara) induced with 1% arabinose. After 1 h cells were fixed, labelled as described in
Materials and Methods, images taken by confocal microscopy and analysed with the plugin. Between 200 and 400 cells per condition were counted and data correspond to median ± standard error from three independent experiments. Non‐parametric, one‐way ANOVA, Kruskal–Wallis test was performed, with Dunn's multiple comparisons test, ****
P < 0.0001, ***
P < 0.001, *
P < 0.05.