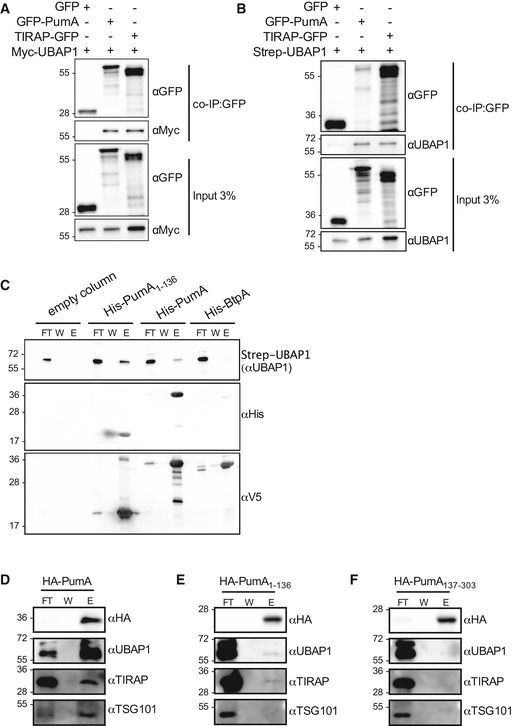
Figure 6. Identification of UBAP1 as a novel host protein targeted by the bacterial TIR domain of PumA.
-
A, BCo‐immunoprecipitation (co‐IP) assay from cells expressing Myc‐UBAP1 (A) or Strep‐UBAP1 (B) with either GFP, GFP‐PumA or TIRAP‐GFP. The co‐IPs were revealed using an anti‐Myc (A) or anti‐UBAP1 (B) antibodies, the fractions bound to GFP‐trapping beads using an anti‐GFP antibody and the inputs using anti‐Myc, anti‐GFP or anti‐UBPA1 antibodies as indicated.
-
CPull‐down assay using extracts from cells expressing Strep‐UBAP1 against His‐PumA or His‐PumA1–136 immobilized on a Ni‐NTA resin. Empty column was used as a control for non‐specific binding. Interactions were visualized by Western blotting using anti‐UBAP1 antibody, and column binding with anti‐His (middle blot), followed by anti‐V5 (lower blot), necessary for detection of BtpA, which for reasons we do not understand cannot be easily detected with the anti‐His antibody (Appendix Fig S5B).
-
D–FEndogenous co‐IP from cells expressing (D) HA‐PumA, (E) HA‐PumA1–136 and (F) HA‐PumA137–303. The fractions bound to HA‐trapping beads were probed with anti‐HA, anti‐UBAP1, anti‐TIRAP and anti‐TSG101 antibodies. Non‐bound fraction (FT), last wash (W) and elution (E) are shown for each sample and the molecular weights indicated (kDa).
Source data are available online for this figure.
