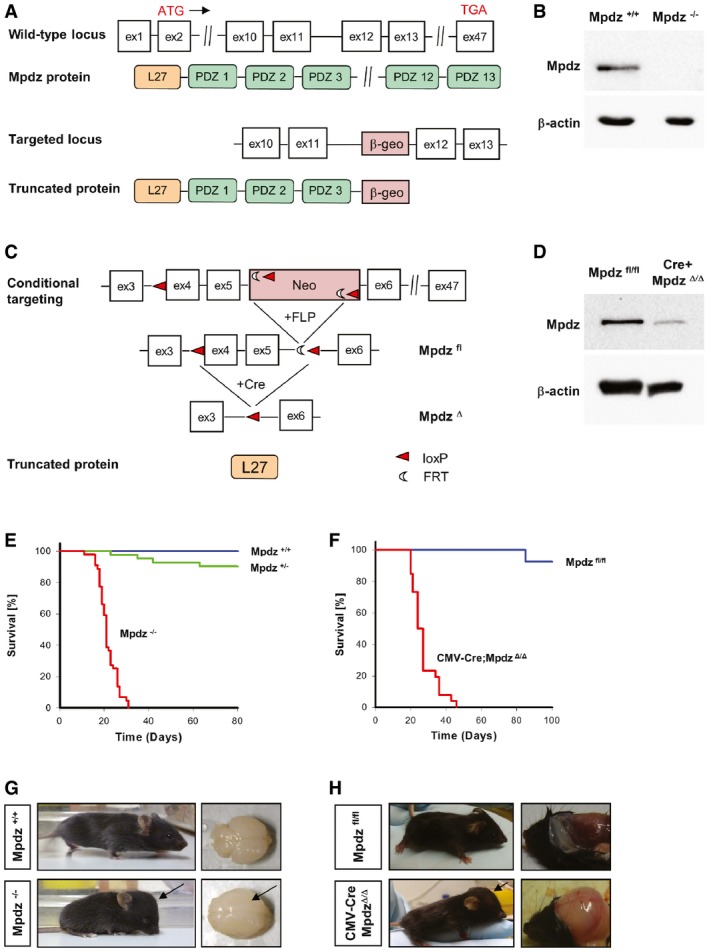
Figure 1. Generation of global and conditional Mpdz knockout mice.
-
ASchematic representation of the Mpdz gene locus and the translated protein. The numbered boxes represent exons 1–47 of the wild‐type allele. The relative position of the translational start and stop sites is indicated at exon 2 and exon 47, respectively. A gene‐trap cassette (β‐geo) was inserted into intron 11–12 leading to a stop signal that truncates the Mpdz protein after the third PDZ domain.
-
BWestern blotting to detect Mpdz protein in brain lysates of littermate wild‐type and global knockout Mpdz mice.
-
CSchematic drawing of the conditional Mpdz gene targeting strategy. LoxP sites flanking exon 4 and a neomycin resistance cassette were inserted by homologous recombination. Transgenic mice were crossed with Flp deleter mice to remove the FRT‐flanked neomycin cassette. Cre recombinase removes exons 4 and 5 leading to a frameshift and a nonsense mutation. This truncates the Mpdz protein after the L27 domain.
-
DWestern blotting to detect Mpdz protein in brain lysates of Mpdz fl/fl and CMV‐Cre;Mpdz Δ/Δ mice.
-
E, FKaplan–Meier survival analysis of Mpdz −/− vs. Mpdz +/+ mice (n > 41 mice per genotype) and CMV‐Cre;Mpdz Δ/Δ vs. Mpdz fl/fl mice (n > 48 mice per genotype).
-
G, HRepresentative images of Mpdz −/− and Mpdz +/+ mice at postnatal day 27 (P27) and CMV‐Cre;Mpdz Δ/Δ and Mpdz fl/fl mice at P24. Arrows indicate the enlarged and dome‐shaped skull and the enlarged brain hemispheres.
Source data are available online for this figure.
