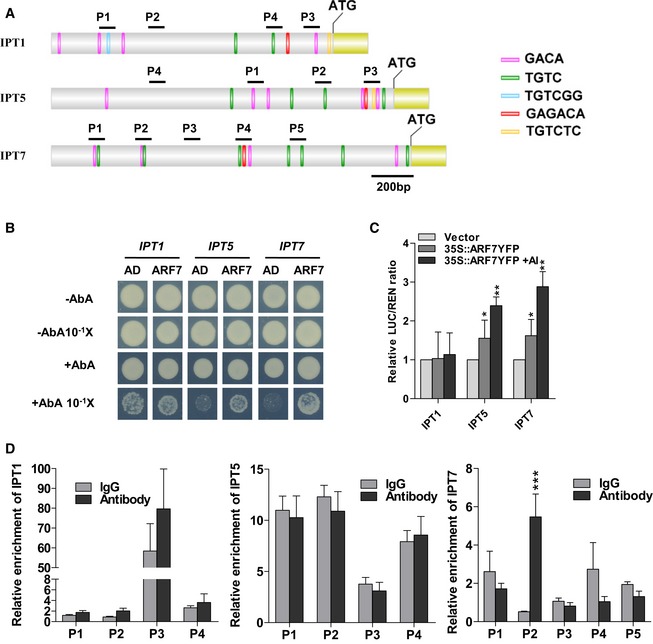
Promoter structure of the IPT genes (IPT1, IPT5, and IPT7) and fragments used in the ChIP assay. The auxin response elements (AuxREs) TGTC, TGTCGG, and TGTCTC on sense strand of the IPT promoters (IPT1, IPT5, and IPT7) are indicated as green, blue, and yellow bars, respectively. The antisense strand AuxRE elements, GACA and GAGACA, are indicated as pink and red bars. Black lines indicate the promoter regions containing AuxREs sequence or not, which are used in the ChIP assay.
Physical interactions of ARF7 with IPT5 and IPT7 promoters in Y1H assays. Yeast expression plasmids pGADT7‐ARF7 (ARF7) are introduced into yeast strain Y1H Gold carrying the reporter gene AbAr under the control of the IPT promoters. The transformants were screened for their growth on the yeast synthetic defined media (SD/‐Leu) in the presence of 75 ng/ml aureobasidin A (AbA) for stringent selection. The empty vector pGADT7 (AD) was included as a negative control. Yeast cultures were diluted (1:10 successive dilution series) and spotted onto plates. In the third lane, yeast strains carrying negative control pGADT7 growing in the presence of the toxic AbA are result from the high concentrated yeast cultures without dilution. The binding of ARF7 to IPT1 promoter is a false‐positive since yeast strains carrying the negative control pGADT7 still grow at the same culture dilution.
ARF7 transactivates the promoters of IPTs in Arabidopsis protoplasts via transient dual‐luciferase assays. The IPT‐LUC reporters are co‐transformed with 35S::ARF7‐YFP plasmid exposed to 10 μM AlCl3 for 12 h or not. The empty vector pBI221 is used as a negative control. * and **: means differ significantly as compared with the respective vector controls at, respectively, P < 0.05 and P < 0.01 (t‐test). Values represent means ± SD (n=3).
ARF7 associated with the promoters of IPT7 in ChIP‐qPCR assay. Chromatins isolated from 35S::MYC‐ARF7 transgenic line were immunoprecipitated with anti‐MYC antibody followed by qPCR to amplify selected regions. Segments P2, P4, and P3 were used as negative controls of IPT1, IPT5, and IPT7 genes, respectively. Mouse IgG was used as a mock control. Input sample was used to normalize the qPCR results in each ChIP. Error bars indicate standard error mean ± SD (n = 3); asterisks in (D) mark significant differences as compared with the IgG mock control (***P < 0.001, t‐test). The experiments are repeated twice with similar results.