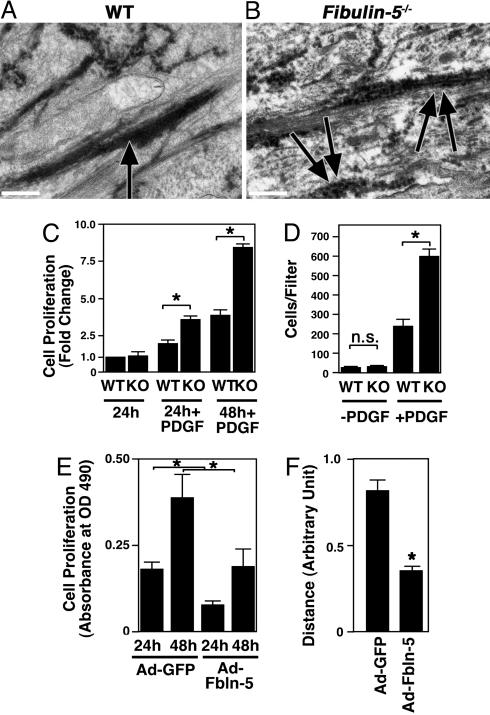
Fig. 5.
Electron micrographs of neointimal lesions and in vitro analysis of fbln-5–/– SMCs. (A and B) Representative photos of electron micrographic observations of ligated arteries from wild-type (A) and fbln-5–/– vessels (B). Note that elastic fibers are continuous and firm in the wild-type vessel (arrow), whereas elastic fibers are irregular and discontinuous in the mutant (double arrows). (Bars, 0.5 μm.) (C) Cell proliferation assays of wild-type (WT) and fbln-5–/– SMCs. WT cells cultured in the serum free condition for 24 h were assigned a value of 1. A fold increase in the indicated condition was shown to allow comparison between the genotype. Data are from three independent experiments performed in triplicate. *, P < 0.05. (D) Modified Boyden chamber assays. Numbers of WT and fbln-5–/– SMCs that migrated to the filter with or without PDGF-BB (50 ng/ml) were counted. Data are from three independent experiments performed in duplicate. n.s., not significant. (E) Cell proliferation assays of fbln-5–/– SMCs infected with the adenovirus expressing GFP (Ad-GFP) or fbln-5 (Ad-Fbln-5). y axis indicates absorbance at OD490 after 24 or 48 h of culture in PDGF-BB (50 ng/ml). Overexpressions of fbln-5 inhibited proliferation of SMCs. Data are from two independent experiments performed in triplicate. (F) In vitro scratch assays of fbln-5–/– SMCs infected with the adenovirus expressing GFP or fbln-5. The distance from the left border of the scratch injury was measured after 6 h of injury. Six to eight measurements were made for each condition. Data are from two independent experiments.