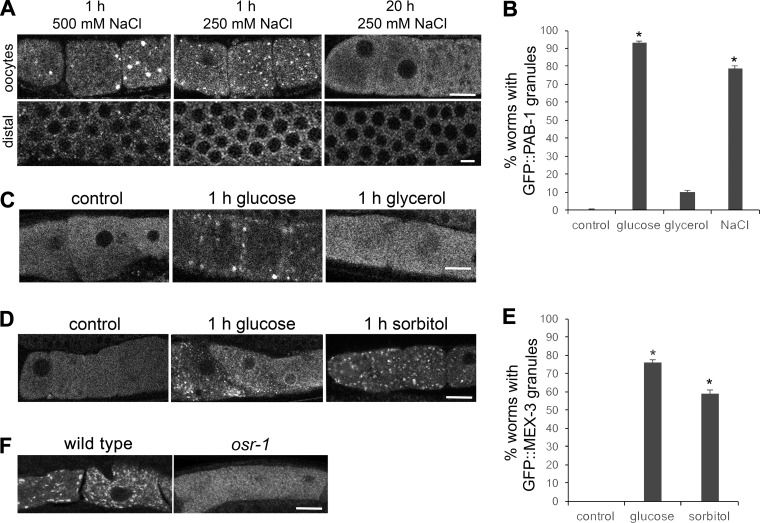
Fig. 3.
Induction of RNP granules by glucose supplementation reflects an osmotic stress response. A: exposure to 250 mM NaCl for 1 h induces cortical GFP::PAB-1 granules in both oocytes and in the distal germ line, but they are not maintained after 20 h of NaCl stress. B: exposure to 250 mM NaCl for 1 h induces GFP::PAB-1 granules in 79% of germ lines, nearly the level observed after exposure to 500 mM glucose (93%). In contrast, exposure to 250 mM glycerol for 1 h induces GFP::PAB-1 granules in only 11% of germ lines, not a significant increase compared with the control. Values are means ± SE (n = 19–66). *P < 0.001, compared with control. C: exposure to 250 mM glycerol for 1 h does not efficiently induce assembly of GFP::PAB-1 granules compared with exposure to 500 mM glucose. D: exposure to 500 mM sorbitol for 1 h induces the assembly of GFP::MEX-3 granules similar to the exposure to 500 mM glucose. E: sorbitol induces the assembly of GFP::MEX-3 granules in 59% of worms, a level not significantly different from the 76% of worms with granules after exposure to 500 mM glucose for 1 h. Values are means ± SE (n = 32–101). *P < 0.001, compared with control. F: MEX-3 granules are detected in significantly fewer worms in osr-1 mutants (10%) exposed to 1 h of 500 mM glucose, as compared with wild type (60%) (n = 25–29). P < 0.001, compared with wild-type control. Scale bars in A, C, D, and F = 7 µm.