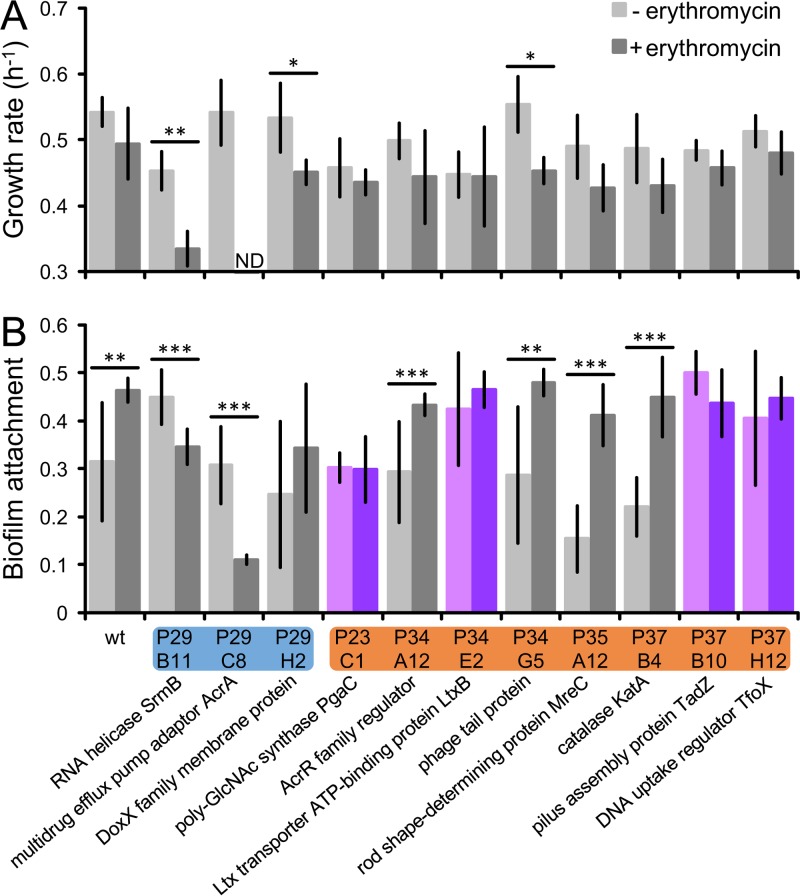
FIG 5.
A. actinomycetemcomitans factors that mediate antibiotic-induced attachment. Growth rates (A) and attachment levels (B) were measured for the wild type (wt) and mutants in half-MIC (+) erythromycin or none (−). y axis in panel A, doublings per hour; y axis in panel B, absorbance (A620) of crystal violet bound to biofilm; blue, mutants that decreased in abundance after erythromycin exposure; orange, mutants that increased in abundance after erythromycin exposure; purple, defective for antibiotic-induced attachment; ND, not detected. Data labels underneath indicate each mutant's disrupted gene product and coordinates in the ordered library. poly-GlcNAc, poly-N-acetylglucosamine; Ltx, leukotoxin. Error bars represent standard deviations (n = 3 to 4 for growth rate; n = 11 to 16 for attachment). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 (two-tailed Student's t test).