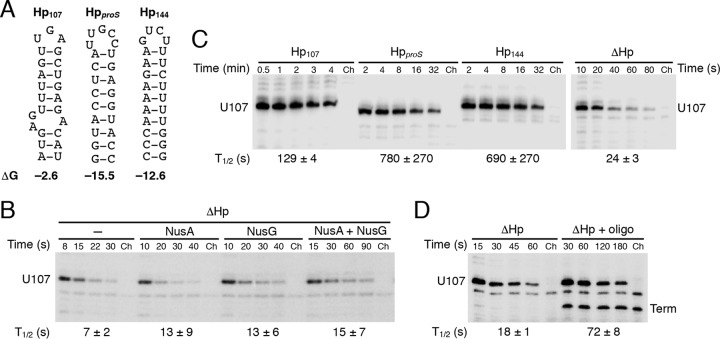
FIG 3.
The presence and strength of the pause hairpin greatly affect pausing at U107. (A) Structures of the U107 (Hp107), proS (HpproS), and U144 (Hp144) hairpins predicted by Mfold (38). (B) Single-round in vitro transcription reactions were performed with a ΔHp DNA template in the absence or presence of 1 μM NusA and/or NusG, as indicated. (C) Single-round in vitro transcription reactions were performed in the presence of 1 μM NusA and 1 μM NusG with templates containing the U107 pause hairpin (Hp107), a hairpin derived from the proS terminator (HpproS), the U144 pause hairpin (Hp144), or no hairpin (ΔHp). Note that the time scale for the ΔHp template is in seconds while those for the other samples are in minutes. (D) Single-round in vitro transcription reactions were performed in the presence of 1 μM NusA and 1 μM NusG with a ΔHp template in the absence or presence of a DNA oligonucleotide complementary to the region just upstream of the U tract. The resulting RNA-DNA hybrid generated a synthetic U107 pause hairpin. The oligonucleotide also resulted in an apparent termination event at position 102 (term). (B to D) Reactions were stopped at the times shown above the lanes. Chase reactions (Ch) were extended for an additional 10 min at 37°C in the presence of 500 μM (each) NTPs. The position of the U107 pause transcript is marked. Pause half-life (t1/2) values and standard deviations are shown at the bottom of each set of lanes. Each experiment was performed at least twice and representative gels are shown.