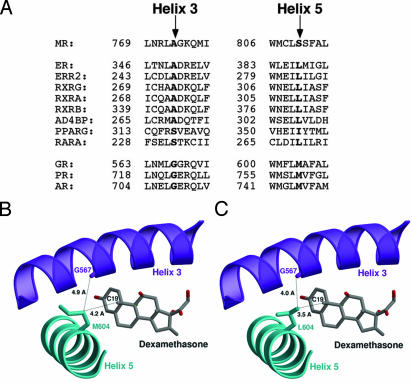
Fig. 1.
Structural model for H3–H5 interaction in GRL604. (A) Coconservation of H3–H5 residues in NRs. The H3 and H5 amino acid sequences of selected NRs were aligned by using clustal w (26), and the residues corresponding to serine 810 on H5 and alanine 773 on H3 in MR are highlighted. Receptors bearing leucine at the H5 position frequently have alanine at the H3 position, whereas receptors bearing methionine at the H5 position have glycine at the H3 position. ER, estrogen receptor; ERR2, estrogen-related receptor type 2; RXRG, rexinoid receptor γ, α, and β; AD4BP, adrenal 4 binding protein (also known as SF1, steroidogenic factor 1); PPARG, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ; RARA, mouse retinoic acid receptor α; AR, androgen receptor. (B) Ribbon drawing of the wild-type GR-LBD (19). H3 is colored in purple, H5 in cyan, and dexamethasone in gray. The steroid, the side chain of Met-604, and the carbonyl oxygen of the Gly-567 main chain are shown as ball-and-stick models and are labeled accordingly. The figure shows that the Met-604 side chain points away from the ligand and is too far from Gly-567 to be in vdW contact. (C) Ribbon drawing of the GRL604 mutant. Unlike Met-604, the side chain of Leu-604 is in vdW contact with the carbonyl oxygen of the Gly-567 main chain. The structure of the GRL604 mutant was generated in silico by replacing Met-604 against leucine. Figures were prepared with the programs molscript, bobscript, and raster3d.