Figure 2. LDHA silencing does not affect oxidative phosphorylation, but attenuates glycolysis in HCT116 cells.
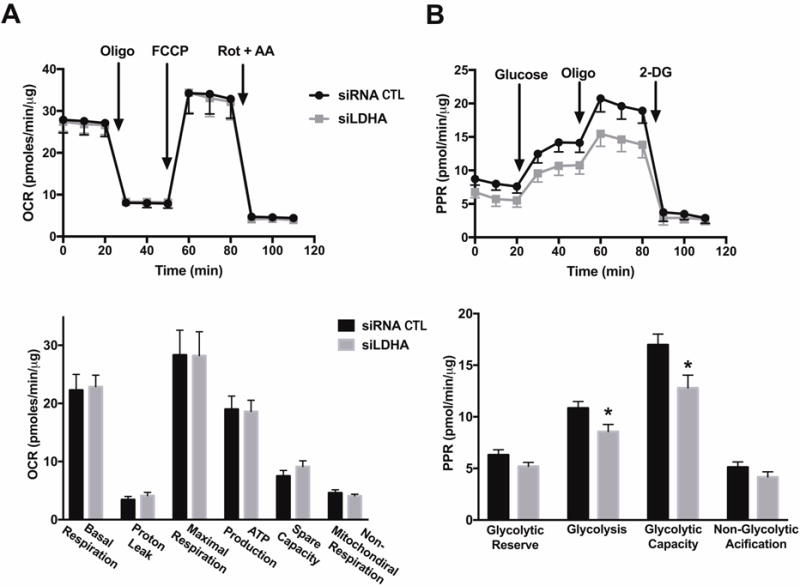
HCT116 cells were transiently transfected with 20 nM nontargeting (siRNA, control) or siLDHA for 72 h. Lipofectamine RNAiMAX was used as the transfection reagent. Extracellular Flux Analysis was then performed. (A) Oxygen consumption rate (OCR) in HCT116 cells transfected with either nontargeting or siLDHA (FCCP: carbonyl cyanide 4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenylhydrazone, a mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation uncoupler; Rot: rotenone; and AA: antimycin A; inhibitors of complex I and III, respectively; top panel). Comparison of cellular bioenergetics parameters based on OCR (bottom panel). (B) Changes in the prolife of proton production rate (PPR) in HCT cells subjected to either siRNA or siRNA silencing of LDHA (oligo: oligomycin, an inhibitor of ATP synthase; 2-DG: 2-deoxy-D-glucose; an inhibitor of glycolysis; top panel). Comparison of cellular bioenergetics parameters based on PPR (bottom panel). Data represent mean ± SEM. n = 4–6 for each group. *P < 0.05 vs. siRNA (based on two-tailed Student’s t-test for pairwise comparison).
