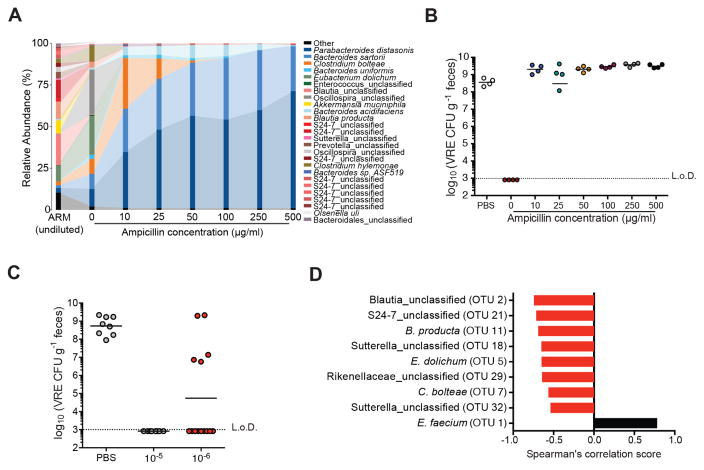
Figure 4. Ampicillin-sensitive bacterial strains within ARM confer resistance to VRE.
(A–B) Fecal suspensions of ARM were diluted 10−5-fold and grown on plates containing 0, 10, 50, 100 and 500 μg/ml of ampicillin. (A) Bacterial composition of cultured fecal fractions. Each bar corresponds to pooled cultures from 3 plates per group. (B) Ampicillin-treated mice were administered PBS or cultured fecal fractions from each group by oral gavage on three consecutive days starting on day 2 of ampicillin treatment and challenged with VRE the day following the third gavage. VRE density in fecal samples was determined 3 days after infection (n = 4 mice per group). (C) VRE levels 3 days post challenge of ampicillin-treated mice inoculated with 10−5 and 10−6 plate cultures as described in (B) (n = 8–14 mice per group). (D) Spearman correlation of OTUs associated with resistance to VRE colonization. OTUs with P values < 0.05 are plotted. L.o.D., limit of detection. See also Figures S3 and S4 and Table S1.