Table 3.
Features of recent small-molecule allosteric PTP inhibitors
| BCI: DUSP6 inhibitor | Compound 211: CD45 inhibitor | SHP099: SHP-2 inhibitor | MSI-1436: PTP1B inhibitor | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical structure |
|
|
|
|
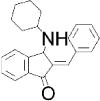
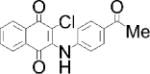
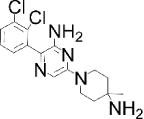
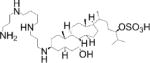
| Special features | Inhibits FGF signaling in zebrafish embryo reporter assay; inhibits ERK-mediated DUSP6 activation; induces death of human ALL cancer cells | Potent, selective; a single 3 mg/kg dose i.p. reduced inflammation in mouse delayed-type hypersensitivity model | Potent, highly selective, orally bioavailable; 75–100 mg/kg p.o. for 10 days decreased tumor cell growth in mouse xenograft models | Binds disordered PTP1B C-terminus, 5 mg/kg i.p. every 3 days inhibited breast tumor growth and metastasis in xenograft models; in Phase I Trial for metastatic breast cancer |
| Potency & selectivity | EC50=10.6 μM in zebrafish assay; inhibits DUSP6 and DUSP1, but not DUSP5, CCDC25B, PTP1B or VHR | CD45 IC50 =290 nM; no inhibition of PTPs LAR, PTP1B, RPTPσ, SHP-1 or DUSP22 | SHP-2 IC50=71 nM; IC50>100 μM on panel of 21 PTPs; IC50>10 μM on panel of 66 kinases; no reactivity against most targets in preclinical safety pharmacology panel up to 30 μM | PTP1B IC50 and Ki=600 nM; 10-fold selective for PTP1B vs TCPTP; 30-fold selective vs CD45, even greater for LAR & PTP-PEST; no activity on RPTPα or RPTPμ |
| Discovery | BCI identified in screen of 5,000 diverse compounds using live zebrafish embryo reporter for FGF activity; DUSP6 identified as molecular target; analog BCI-215 with similar potency and reduced toxicity identified in SAR analysis using zebrafish reporter assay | 120,000-compound in silico screen of NCI database for potential binding in groove at interface between CD45 D1 & D2 domains; hits tested for in vitro inhibition of intracellular region of CD45 using SRC peptide substrate; hit 37p analog 211 identified by SAR analysis | 100,000-compound screen of Novartis archive for inhibitors of full-length SHP-2 (in the presence of 0.5 μM bisphosphorylated IRS-1 peptide) but not SHP-2 PTP domain using DiFMUP substrate; medicinal chemistry improved initial hit SHP836 to SHP099 | Identified as appetite suppressant in mice; PTP1B later identified as molecular target |
| MOA | Inhibits substrate-induced stimulation of DUSP6 activity; predicted to bind crevice between general acid loop and helix α7 in low-activity DUSP6 form, preventing positioning of residue Asp262 for catalysis | Irreversible, non-competitive; causes conformational change of protein; predicted to bind in goove near interface between CD45 D1 & D2 domains | Binds allosteric pocket formed at interface of C-terminal SH2, N-terminal SH2 and PTP domains when enzyme is in closed, inactive conformation; stabilizes enzyme in inactive conformation | Reversible, non-competitive; likely binds to C-terminal helix α9′ and to another site close to catalytic region; induces conformational change in protein |
| Binding validation | Binding predicted by molecular docking | Circular dichroism suggested dramatic change in secondary structure of CD45 but not LAR; binding supported by mutation | Differential scanning fluorimetry: ΔTm=3.02°C; Xray co-crystallization with SHP-2 aa 1–525 (PDB 5EHP); mutation | Binding & conformational change shown by ITC, trypsin sensitivity, FRET, NMR spectroscopy and mutation |
| Cellular efficacy & specificity | Promoted FGF signaling in zebrafish embryos; restored ERK phosphorylation in phorbol ester-stimulated HeLa cells overexpressing DUSP6 (EC50=13.3 μM) or DUSP1 (EC50=8.0 μM), while inactive analogs did not; induced ALL cancer cell death (IC50=2.1 μM) | At 0.5 μM, increased phosphorylation of LCK-Y394 in Jurkat but not CD45-null J.45 T cells, and blocked TCR-induced phosphorylation of LCK-Y394, ZAP-70-Y319 and ERK1/2, IL-2 release and proliferation of primary mouse splenocytes | At [low-μM], slowed growth of hematopoietic cancer cells dependent on RTK or JAK1/2 signaling & colorectal cancer cells sensitive to Lapatinib; did not inhibit growth of cells carrying mutations in RAS or BRAF or KYSE520 cells carrying SHP-2-T253M/Q257L mutant | At [low-μM], blocked HER2 activation in MCF10A mammary epithelial cells; reduced migration of HER2 positive cell lines but not in MDF10A-NeuNT cells carrying PTP1B-L192A/S372A mutant; MSI-1436, but not inactive analog, pulled-down PTP1B from tumor lysates |
| Refs. | [40,42,43] | [45] | [46,47] | [48,50] |
BRAF, B-raf proto-oncogene; HAD, haloacid dehalogenase; HER2, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; IRS-1, insulin receptor substrate 1; JAK, Janus kinase; NIH, National Institutes of Health; MLPCN, Molecular Libraries Probe Centers Network; NCI, National Cancer Institute; PPM1A, protein phosphatase magnesium-dependent 1A; Refs., references; RTK, receptor tyrosine kinase; SCP1, small C-terminal domain phosphatase 1; SRC, proto-oncogene tyrosine protein kinase; ZAP-70, zeta-chain-associated protein kinase of 70 kDa
