Abstract
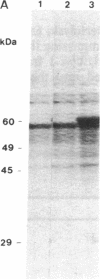
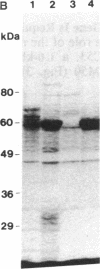
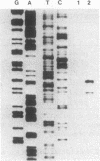
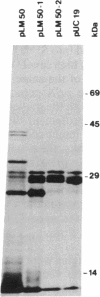
We have isolated, by molecular cloning and genetic complementation of a listeriolysin-negative mutant, a gene required for the expression of this virulence factor in Listeria monocytogenes. The mutant strain SLCC53, which was nonhemolytic and avirulent, harbored a deletion of 450 base pairs located approximately 1500 base pairs upstream of the listeriolysin gene. No transcripts corresponding to the listeriolysin gene were detected in the mutant. DNA sequencing of this region from the hemolytic strain EGD revealed that the region deleted in the mutant would abrogate expression of a 27-kDa polypeptide. Introduction of a recombinant plasmid expressing this 27-kDa polypeptide restored hemolytic activity to the mutant and increased the hemolytic activity of the wild-type L. monocytogenes strain EGD. We have designated the gene encoding the 27-kDa polypeptide prfA, for positive regulatory factor of listeriolysin (lisA) expression. The prfA gene regulates transcription of the lisA gene positively.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chakraborty T., Huhle B., Bergbauer H., Goebel W. Cloning, expression, and mapping of the Aeromonas hydrophila aerolysin gene determinant in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):368–374. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.368-374.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Yagi Y., Dunny G. M., Schultz S. K. Characterization of three plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid molecules in a strain of Streptococcus faecalis: identification of a plasmid determining erythromycin resistance. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):283–289. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.283-289.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domann E., Chakraborty T. Nucleotide sequence of the listeriolysin gene from a Listeria monocytogenes serotype 1/2a strain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6406–6406. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Sansonetti P. Transposon mutagenesis as a tool to study the role of hemolysin in the virulence of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):50–55. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.50-55.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kathariou S., Metz P., Hof H., Goebel W. Tn916-induced mutations in the hemolysin determinant affecting virulence of Listeria monocytogenes. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1291–1297. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1291-1297.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn M., Kathariou S., Goebel W. Hemolysin supports survival but not entry of the intracellular bacterium Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):79–82. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.79-82.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leimeister-Wächter M., Chakraborty T. Detection of listeriolysin, the thiol-dependent hemolysin in Listeria monocytogenes, Listeria ivanovii, and Listeria seeligeri. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2350–2357. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2350-2357.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leimeister-Wächter M., Goebel W., Chakraborty T. Mutations affecting hemolysin production in Listeria monocytogenes located outside the listeriolysin gene. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Nov;53(1-2):23–29. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90360-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengaud J., Vicente M. F., Chenevert J., Pereira J. M., Geoffroy C., Gicquel-Sanzey B., Baquero F., Perez-Diaz J. C., Cossart P. Expression in Escherichia coli and sequence analysis of the listeriolysin O determinant of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):766–772. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.766-772.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengaud J., Vicente M. F., Cossart P. Transcriptional mapping and nucleotide sequence of the Listeria monocytogenes hlyA region reveal structural features that may be involved in regulation. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3695–3701. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3695-3701.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monack D. M., Arico B., Rappuoli R., Falkow S. Phase variants of Bordetella bronchiseptica arise by spontaneous deletions in the vir locus. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Dec;3(12):1719–1728. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00157.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mounier J., Ryter A., Coquis-Rondon M., Sansonetti P. J. Intracellular and cell-to-cell spread of Listeria monocytogenes involves interaction with F-actin in the enterocytelike cell line Caco-2. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):1048–1058. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.1048-1058.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Jacks P. S., Hinrichs D. J. Role of hemolysin for the intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1459–1471. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocourt J., Alonso J. M., Seeliger H. P. Virulence comparée des cinq groupes génomiques de Listeria monocytogenes (sensu lato). Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1983 May-Jun;134A(3):359–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. J., LaPenta D., Chen C., Cleary P. P. Coregulation of type 12 M protein and streptococcal C5a peptidase genes in group A streptococci: evidence for a virulence regulon controlled by the virR locus. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):696–700. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.696-700.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soberon X., Covarrubias L., Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. IV. Deletion derivatives of pBR322 and pBR325. Gene. 1980 May;9(3-4):287–305. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90328-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Portnoy D. A. Actin filaments and the growth, movement, and spread of the intracellular bacterial parasite, Listeria monocytogenes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1597–1608. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wick M. J., Frank D. W., Storey D. G., Iglewski B. H. Identification of regB, a gene required for optimal exotoxin A yields in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Mar;4(3):489–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00615.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]