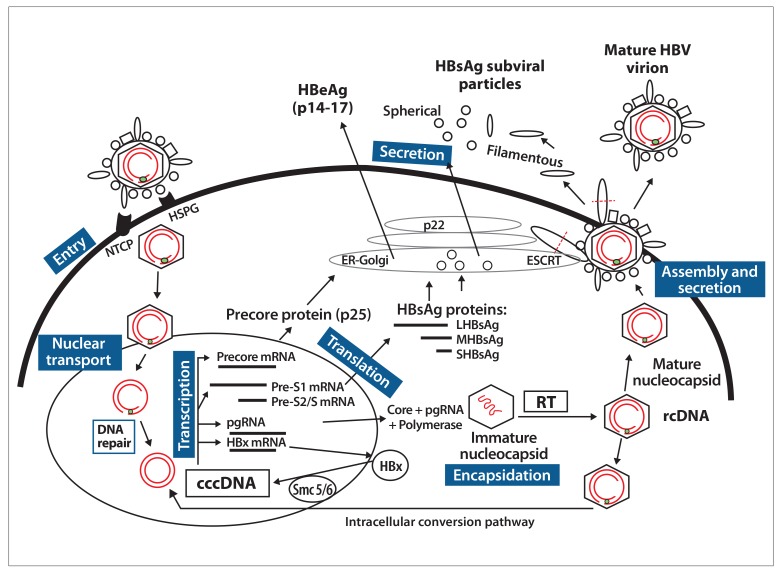
Figure.
Life cycle of hepatitis B virus.
Entry: HBV is tethered to HSPG, and this facilitates entry via its receptor NTCP. HBV is endocytosed into the cell and released into the cytoplasm of the hepatocyte.
Nuclear transport: After uncoating of the HBV virion in the cytoplasm, the partially double-stranded DNA is transported to the nucleus, where its genomic rcDNA is repaired by host enzymes to form cccDNA, the template for HBV replication.
Transcription: cccDNA generates pgRNA that produces the core protein and viral polymerase, precore mRNA that produces HBeAg, and the subgenomic RNAs that produce HBsAg and HBx proteins.
Encapsidation: The HBV core protein (core) is critical for formation of replication complexes containing the pgRNA and polymerase, forming an immature nucleocapsid. After RT of the pgRNA, a mature nucleocapsid containing DNA is formed. Core is also required for intracellular trafficking, and encapsidated HBV genomes are imported back into the nucleus via the intracellular conversion pathway, partly replenishing the pool of cccDNA minichromosomes.
Assembly and secretion: Mature nucleocapsids are enveloped with HBsAg (pre-S1, pre-S2, and S) proteins through the ESCRT machinery in the Golgi, resulting in the secretion of mature virions and releasing excess HBsAg as filamentous subviral particles. The HBsAg subviral 22-nm particles are produced in great excess and secreted via the ER-Golgi apparatus. HBeAg is a soluble and secreted product of precore mRNA.
cccDNA, covalently closed circular DNA; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; ESCRT, endosomal sorting complex required for transport; HBeAg, hepatitis B e antigen; HBsAg, hepatitis B surface antigen; HBV, hepatitis B virus; HBx, hepatitis B x; HSPG, heparan sulfate proteoglycans; LHBsAg, large hepatitis B surface antigen; MHBsAg, medium hepatitis B surface antigen; mRNA, messenger RNA; NTCP, sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide; pgRNA, pregenomic RNA; rcDNA, relaxed circular DNA; RT, reverse transcription; SHBsAg, small hepatitis B surface antigen; smc, structural maintenance of chromosomes.