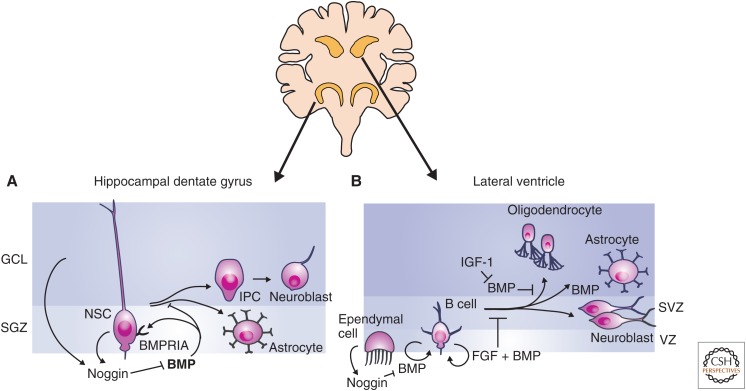
Figure 2.
Transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) family signaling in neural stem cells. Adult neural stem cells (NSCs) are primarily located in the subgranular zone (SGZ) of the hippocampal dentate gyrus and the subventricular zone (SVZ) lining the lateral ventricles. (A) Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling promotes the maintenance of the NSC state in the SGZ, and signaling through BMPRIA inhibits NSC proliferation. NSCs of the SGZ produce the BMP inhibitor Noggin. Loss of BMP signaling through repression of BMPRIA or inhibition of BMP signaling results in the formation of intermediate progenitor cells (IPCs), which differentiate into neuroblasts and astrocytes in vivo. BMP is drawn in bold in the dentate gyrus to indicate increased levels of BMP expression relative to SVZ. (B) In the SVZ, NSCs are called B cells and are maintained as slowly cycling NSCs by BMP and fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signaling. Noggin is produced by ependymal cells and inhibits of BMP signaling. BMP signaling promotes maintenance of the NSC state, but once cells begin to proliferate and differentiate, BMP signaling can also promote astrocyte differentiation. GCL, Granular cell layer.