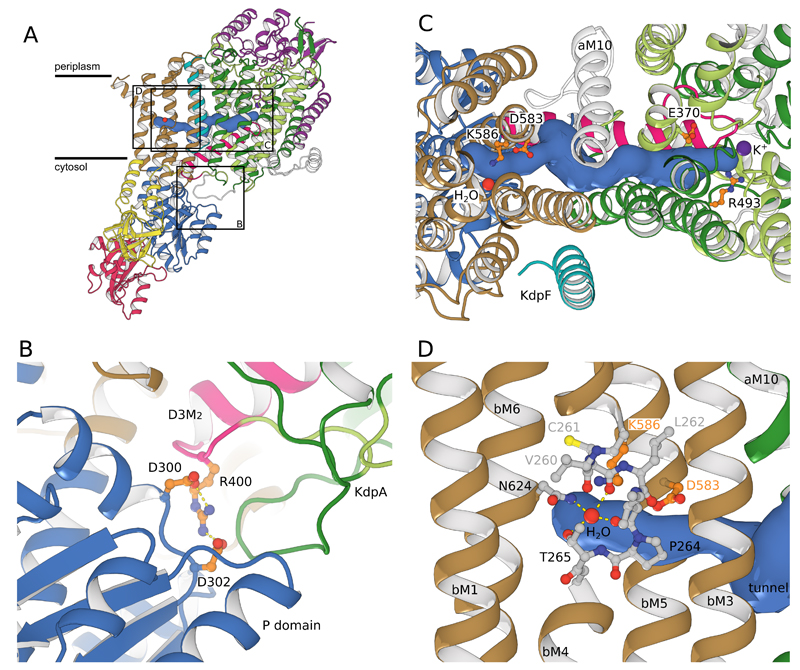
Figure 3. Coupling KdpA and KdpB.
(A) A tunnel (>1.4Å radius, blue surface) connects the water molecule in KdpB to the K+ ion in KdpA. The coupling helix (pink) runs adjacent to the tunnel on the cytosolic side of the membrane. (B) Salt bridges attach the coupling helix to the P-domain of KdpB (blue). (C) Closeup from the periplasmic side shows charged residues at either end of the tunnel: Glu370/Arg493 in KdpA and Asp583/Lys586 in KdpB. The tunnel could facilitate charge transfer between these two sites. D) In KdpB, an unwound portion of transmembrane helix bM4 (shown in stick representation) forms a binding site similar to other P-type ATPases. The modeled water is coordinated by main chain carbonyls from bM4 and side-chain oxygens from Thr265 and Asn624.