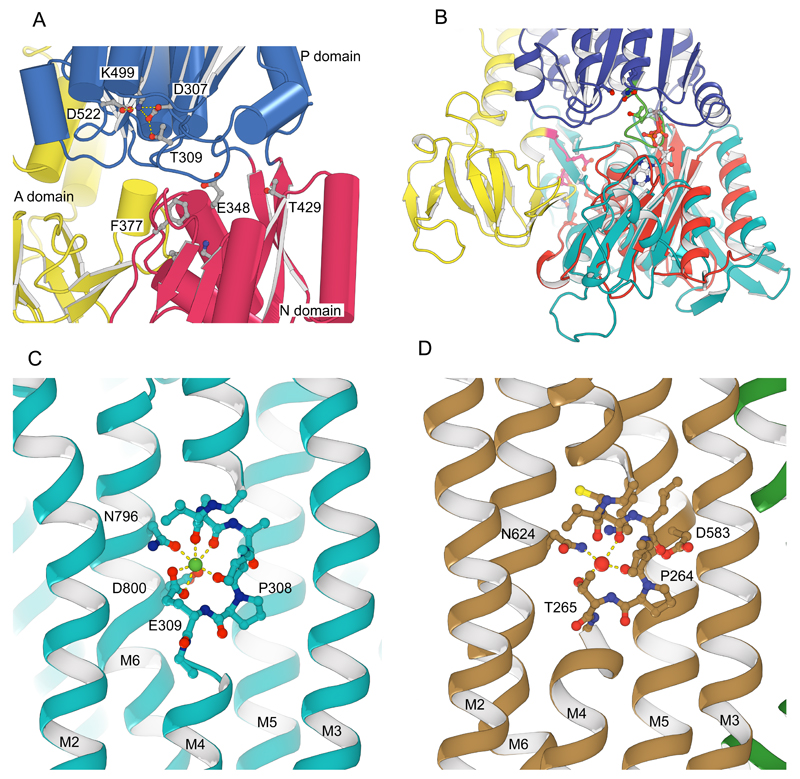
Extended Data Figure 4. Comparison of KdpB and SERCA1a.
(A) In the P-domain of KdpB (blue), there is no evidence for phosphorylation of the catalytic Asp307 which is in a binding network with Lys499, Asp522 and Thr309. The location of the nucleotide binding pocket is illustrated by some of the conserved residues (Glu348, Phe377 and Thr429) expected to interact with ATP in the N-domain (red). (B) Overlay of the N-domains of KdpB (red) and SERCA1a (cyan, 1T5T)56 with bound nucleotide (ADP-AlF4). This overlay illustrates how, if nucleotide were bound to the corresponding site in KdpB, the phosphate groups would clash with the conserved catalytic loop (DKTGTLT in green). The TGES162 loop of KdpB is colored pink. Taken together, the Asp307 binding network and the positional decoupling of the A-domain from the rest of the structure indicate that KdpB is in an E1 state in which the Asp307 remains unphosphorylated and the N-domain nucleotide binding site is empty15,56–58. (C) The binding site for Ca(II) (green sphere)15 in the transmembrane domain of SERCA1a (1T5T) consists of main chain carbonyls from the broken M4 helix near the canonical Pro308 as well as side chain densities from the neighboring M6 helix (Asn796 and Asp800). The second Ca2+ ion in the Ca(I) site is not shown, but involves additional ligands from the M5 helix. (D) The water site (red sphere) in the transmembrane domain of KdpB involves the residues homologous to SERCA1a in a very similar configuration. Namely, the main chain carbonyls on M4 near Pro264 and the side chain of Asn624. The side chains of Asp583 and Lys586 from M5 are also nearby, which align with Asn768 and Glu771 in SERCA1a that bind Ca(I).