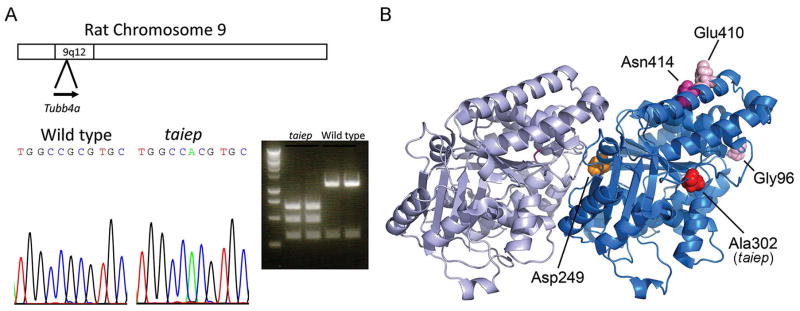
Fig. 4. Identification of Tubb4a mutation in taiep rat.
A) Previous work had localized the causative gene in the taiep mutant to rat chromosome 9q12. Analysis of candidate genes revealed Tubb4a, which is mutated in several patients with hypomyelination. Sequencing of taiep mutant rats and normal controls revealed an A to G mutation that changes Ala302 to Thr. The mutation also introduces a MscI restriction enzyme site. PCR fragments were generated from taiep rat and wild type littermate cDNA, and both fragments were digested with the MscI restriction enzyme, indicating a homozygous mutation in taiep. B) The crystal structure of α- and β-tubulins was used to indicate the position of the Ala302 residue that is mutated in the taiep rat and the Asn414 residue mutated in our patient. Additionally the position of the classical H-ABC mutation (Asp249) and two other patients with isolated hypomyelination (Glu410 and Gly96) are shown. The classical H-ABC mutation is located at the α-β interface where most H-ABC mutations are located, whereas the taiep mutation and the mutations observed in patients with isolated hypomyelination are located at the lateral side of β-tubulin.