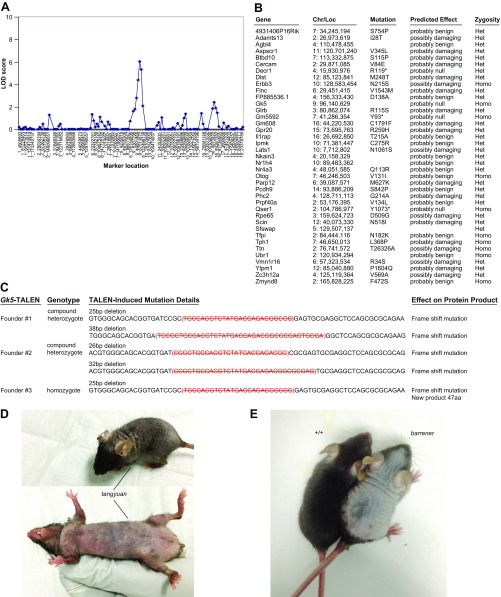
Fig. S2.
Gk5 deficiencies cause the alopecia phenotype. (A) Bulk segregation analysis identified the toku mutation within a critical region on chromosome 9. LOD scores at each marker location are shown. (B) Other mutations in the toku stock. Whole-exome HiSeq sequencing of the index toku mouse identified 39 mutations. Effects of missense mutations on protein function were predicted by PolyPhen-2. (C) DNA sequence of the Gk5 locus from the F0 Gk5-TALEN mice. Strikethrough denotes deleted nucleotides. The changes in amino acid sequence are described in the text. (D) The tangyuan mouse exhibits hair loss. The tangyuan phenotype was mapped to a mutation (G to A at 96,150,797 bp) of a critical splice donor site (1 bp from exon) in Gk5, resulting in the deletion of exon 9. (E) The barrener mouse exhibits hair loss. A wild-type littermate is shown for reference. The barrener phenotype was mapped to a mutation (T to C at 96,129,096 bp) of a critical splice donor site (2 bp from exon) in Gk5, resulting in the deletion of exon 2.