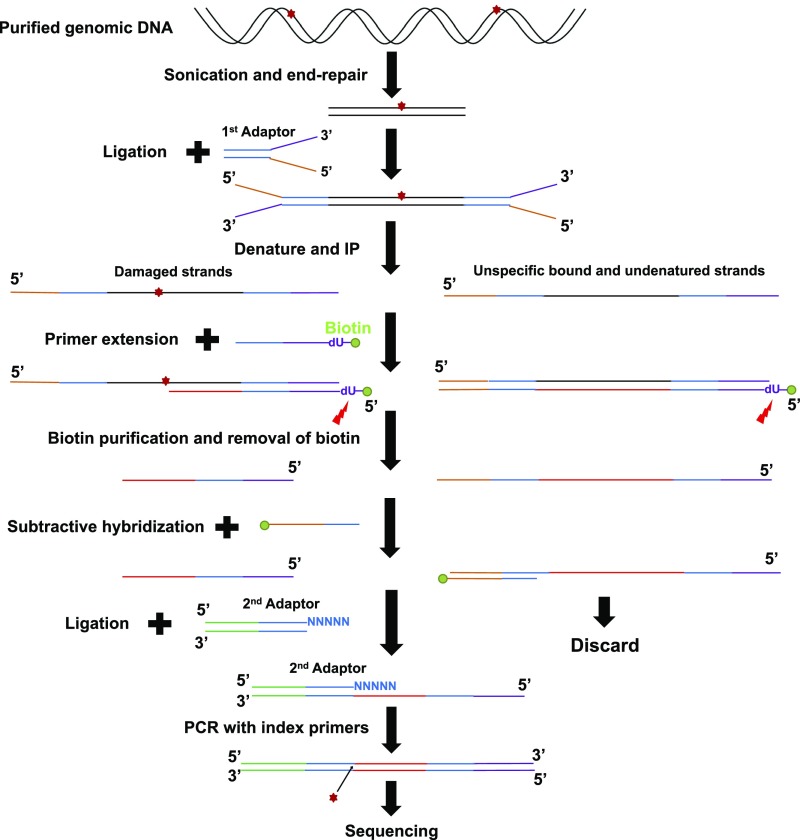
Fig. S1.
Schematic representation of HS–Damage-seq method. Genomic DNA from UV-treated cells was sonicated and subjected to end repair. Then the first adaptor was ligated to these end-repaired fragments. This step was followed by denaturation and IP with an antibody against specific DNA lesion. Next, a biotinylated primer (with a dU base) was annealed to the 3′ end of the first adaptor and extended by a DNA polymerase, which was blocked by DNA damage. The extension products were denatured and purified by streptavidin beads, then eluted by digesting the dU base. The unblocked extension products were then captured by biotinylated oligonucleotides identical to the 5′ end of the first adaptor and removed by streptavidin beads. Purified fragments were ligated to the second adaptor. Finally, the ligation products were amplified with index primers and sequenced.