Figure 4. DPEN + CuSO4 selectively induced clonogenic cell killing in human breast and lung epithelial cancer cells as compared to normal non-transformed human breast and lung epithelial cells. Intracellular labile iron pool is significantly higher in lung cancer cells compared to normal non-immortalized lung epithelial cells.
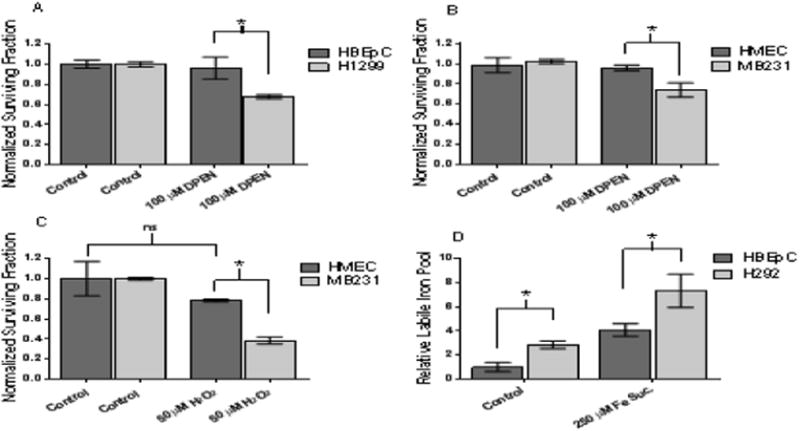
(A) Normal lung epithelial cells (HBEpC) and lung cancer cells (H1299) were treated 100 μM DPEN + 15 μM CuSO4 for 3 hours then subjected clonogenic assay. (B) Normal breast epithelial cells (HMEC) and breast cancer cells (MB231) similarly treated with 100 μM DPEN + 15 μM CuSO4 followed by clonogenic assay. (C) HMEC and MB231 cells were treated for 3 hours with 50 μM H2O2 followed by the clonogenic assay. (D) Relative intracellular labile iron pools measured using Calcein AM dye followed by flow cytometry comparing HBEpC and H292 cells. Cells were pre-treated with 250 μM Fe sucrose or 250 μM DFO as a positive and negative control. *Significantly different. p<0.05; n=3. Errors represent ± 1 SEM.
