Figure 2. IAPP+/+ × APP mice display increased Aβ-immunopositive deposition in the brain.
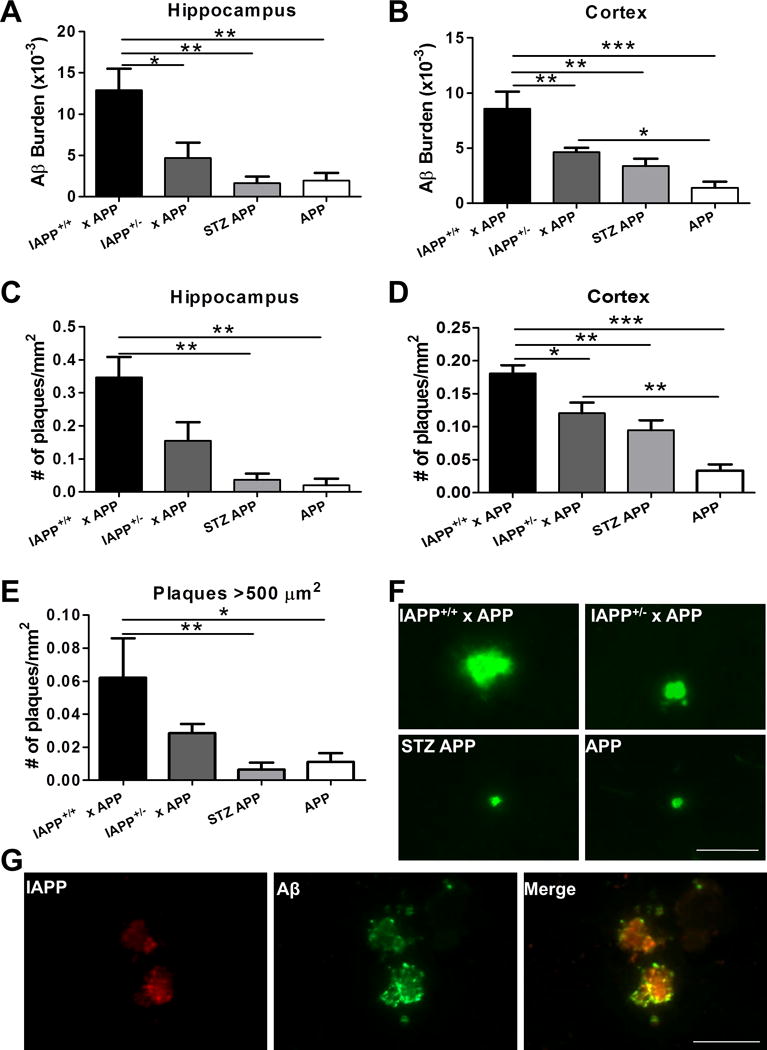
Aβ deposition was analyzed in the brain of transgenic animals over-expressing human IAPP and APP and control animals by immunohistological staining using 4G8 antibody. n=5–10 animals/group; 5 sections/animal. A–B: Brain Aβ burden was quantified as the immune-reactive area per total area analyzed in IAPP+/+ × APP, IAPP+/− × APP, APP animals injected with STZ, and untreated APP mice in hippocampal and cortical areas. C–D: Amyloid plaque density was measured as the number of plaques per mm2 in the hippocampus and cortices. E: Plaques bigger than 500 μm2 were quantified in the brain of experimental and control groups. Data in panel A–E was analyzed by one-way ANOVA, followed by the Tukey’s multiple comparison post-hoc test. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001. F: Representative pictures of amyloid plaques in the cortical area reactive to human anti-Aβ antibody 82E1 in analyzed groups. G: Double immune-staining of IAPP (in red) and Aβ (in green), and co-localization (yellow) in the cortical area of IAPP+/+ × APP transgenic mice. Scale bar: 50 μm.
