FIGURE 7.
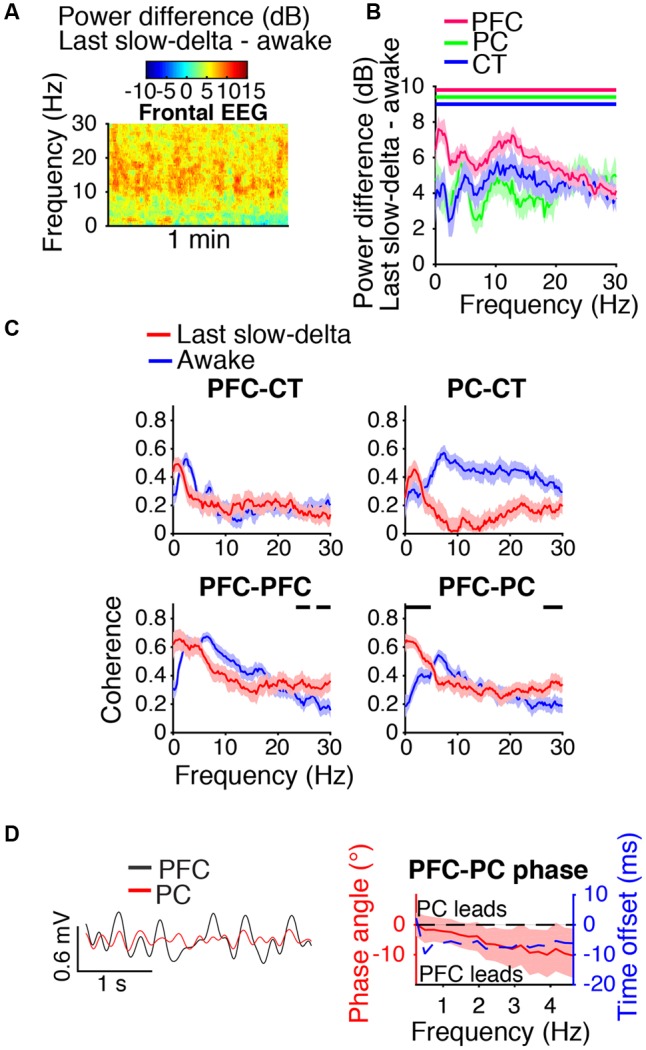
Dynamics during the last minute of elevated slow-delta power. (A) Group difference spectrogram of the frontal EEG during the last minute of elevated slow-delta power. The same period is analyzed in (B–D). (B) Group power difference for PFC (red), PC (green), and CT (blue) LFPs. Shading indicates 95% confidence intervals. Red, green, and blue horizontal lines mark ranges of significant power increase relative to awake baseline for PFC, PC, and CT LFPs, respectively. (C) Group coherence between LFPs during the awake baseline (blue) and last minute of elevated slow-delta power (red) states. Shading indicates 95% confidence intervals, and horizontal lines mark ranges of significant coherence increase from awake baseline. (D) Left: PFC (black) and PC (red) LFPs from a representative animal filtered in the range of significant PFC–PC LFP coherence increase within the slow-delta range shown in (C). Right: Group PFC–PC LFP phase relationship shown for the range of significant PFC–PC LFP coherence increase shown in (C), in terms of phase angle (left y-axis, red line) and time offset (right y-axis, blue dotted line). Shading indicates 95% confidence intervals for phase angle. A negative phase relationship indicates that the first signal leads the second.
