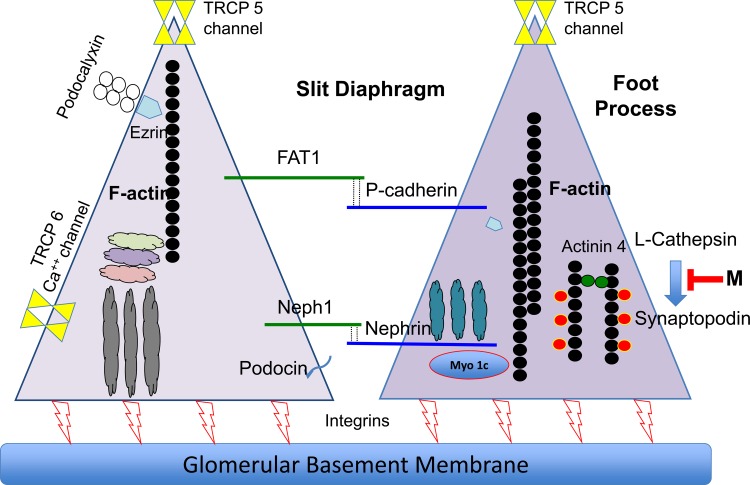
Fig. 5.
Synaptopodin-L-cathepsin blocking peptide: simplified schematic diagram of adjacent podocyte foot processes that comprise the slit diaphragm responsible for creating an albumin filtration barrier. A small peptide-blocking mimotope (“M”) that interferes with L-cathepsin-mediated synaptopodin degradation would be expected to increase podocyte synaptopodin, thereby stabilizing the actin cytoskeleton, which maintains normal foot process and slit diaphragm structure and extracellular signaling and, potentially, reduces proteinuria. Ideally, two blocking peptides would be required to maximally inhibit the synaptopodin-L-cathepsin interaction to effectively support dynamic actin cytoskeletal remodeling.