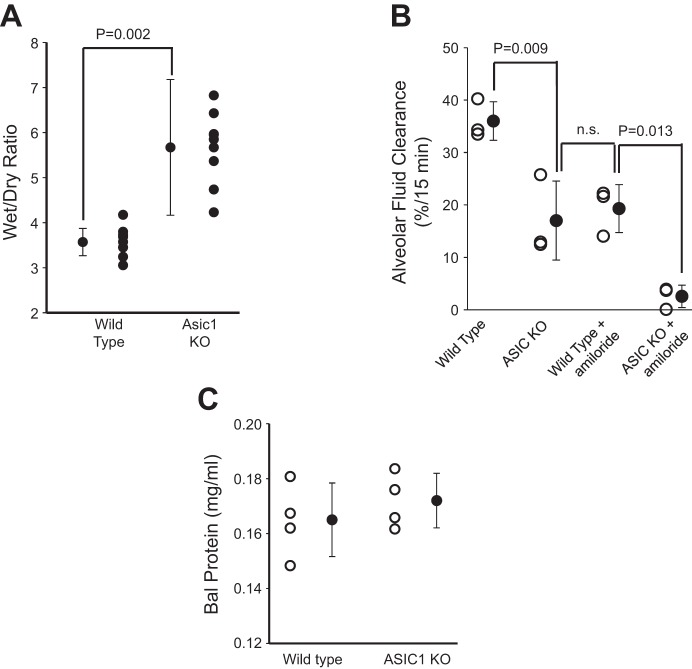
Fig. 14.
ASIC1a KO increases lung water content and reduces alveolar fluid clearance. A: lung wet wt-to-dry wt ratios. Higher wet wt-to-dry wt ratio indicates increased lung water content and decreased alveolar fluid clearance. The difference in the two groups is significant. Data represent n = 8 for each treatment group. B: Evans blue dye assay showed that alveolar fluid clearance was significantly reduced in ASIC1a KO mice compared with wild-type mice. Amiloride blocked about half of AFC in wild-type mice, but there is little residual AFC after amiloride in ASIC1 KO mice. Data represent a total n = 3 mice for each treatment group; n.s., not significant. C: bronchalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid protein from wild-type and ASIC1 KO mice. There is no significant difference in BAL protein between the two groups (n = 4 mice for each treatment group; P = 0.424).