Fig. 4.
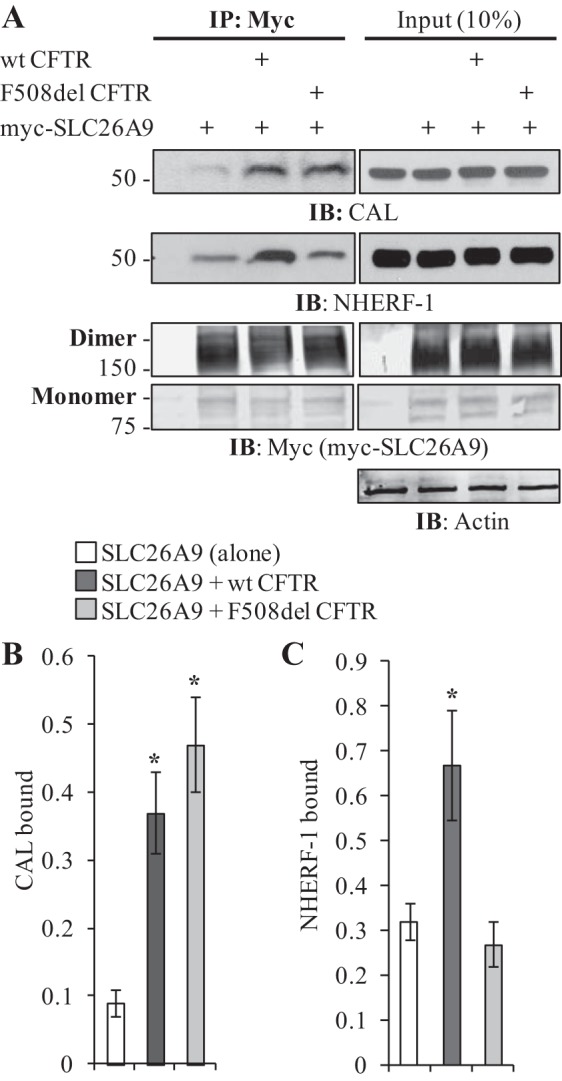
SLC26A9 coimmunoprecipitates the PDZ-domain proteins CAL and NHERF-1. A: differences in myc-SLC26A9’s ability to co-IP NHERF1 and CAL are dependent on the coexpression of CFTR. Coexpression with wt CFTR increases the co-IP of both PDZ-domain proteins, whereas coexpression with F508del CFTR only affects CAL co-IP. Left panels, IP; right panels, Input. Both monomers and dimers of myc-SLC26A9 are shown. Samples were not treated with forskolin before cell lysis. B: quantification of CAL binding indicates either form of CFTR increases myc-SLC26A9’s ability to co-IP CAL. Normalized by total immunoprecipitated myc-SLC26A9 (monomer plus dimer). Averages from 3 independent experiments, *P < 0.05. C: quantification of NHERF1 binding indicates only coexpression with wt CFTR enhances NHERF1 co-IP. Normalized by total immunoprecipitated myc-SLC26A9 (monomer plus dimer). Averages from 3 independent experiments, *P < 0.05.
