Figure 1.
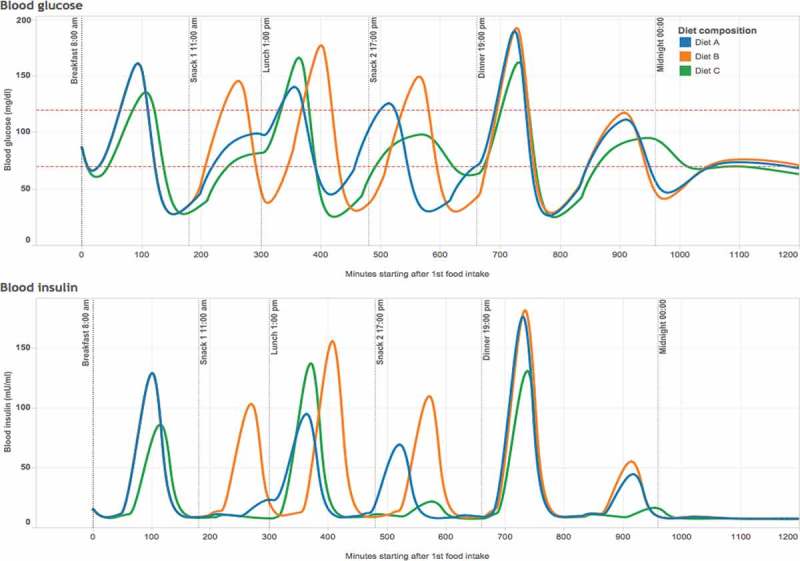
Differences in levels of blood glucose (top) and blood insulin (bottom) in the human body as provoked by diets with identical caloric content, but different compositions of macronutrients.
Notes: Diets were assumed in this model calculation as follows, Diet A (blue): 1670 kcal per day of energy content (7000 kjoules) with a composition of 53% CHO, i.e. 218 grams of CHO; 22% protein; and 25% fat. The CHO content is divided among three equal intakes during the day, i.e. 72.6 g for breakfast, 72.6 g for lunch and 72.6 g for dinner. Diet B (orange): same composition as diet A but adding two snacks, i.e. one apple between breakfast and lunch (34 g of CHO) and one banana between lunch and dinner (30 g of CHO). Diet C (green): the same energy content as in other diets, 1670 kcal per day (7000 kjoules), but with a composition of 38% CHO, i.e. 156 grams of CHO; 32% protein; and 30% fat. The CHO content is again divided into three equal intakes during the day, i.e. 52 g in breakfast, 52 g in lunch and 52 g in dinner. All diets were modeled for a non-diabetic adult of 60 kg of body weight using the web-based simulator of glucose and insulin levels in the human body ‘Glucosim’ developed by the Illinois Institute of Technology [95].
