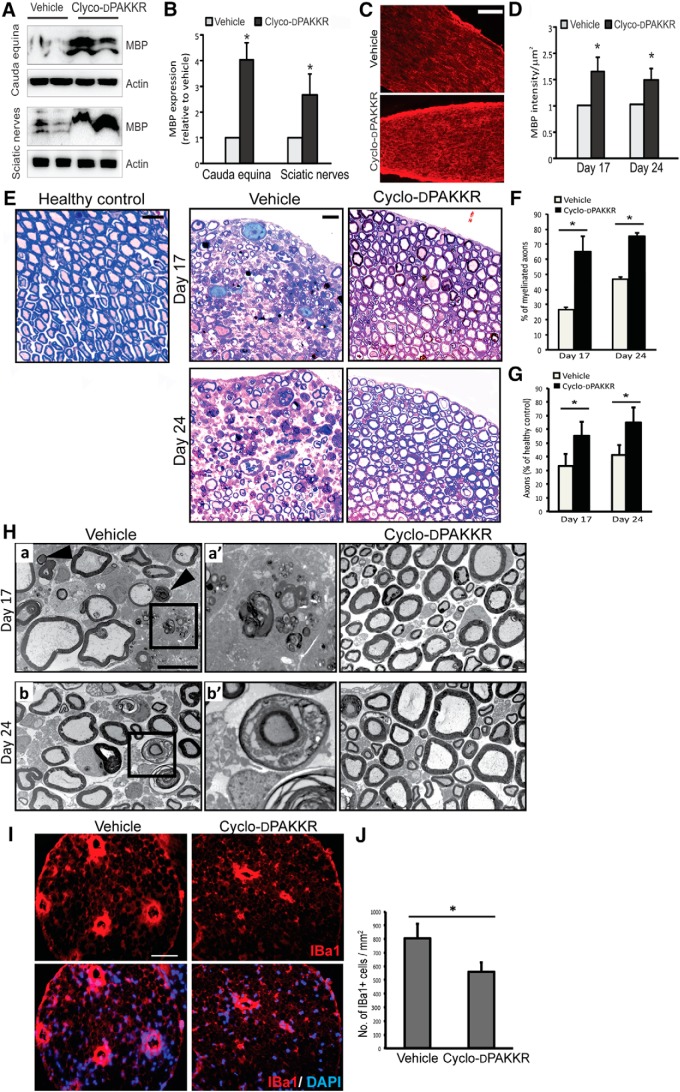
Figure 3.
Cyclo-dPAKKR limits the extent of myelin and axonal pathology in EAN. Analyses of cauda equina or sciatic nerves isolated from age-matched healthy control (no EAN) or rats subjected to EAN at day 17 or day 24 after daily treatment with Cyclo-dPAKKR (10 mg/kg) or vehicle control (data: mean ± SEM, n = 3–4/group/time point, two-way repeated measures ANOVA *p < 0.05). A, B, Western blot (A) and densitometric analyses (B) of Western blot bands from cauda equina and sciatic nerve lysates of EAN rats at day 17. C, D, Immunohistochemistry against the myelin marker MBP (C) and quantitation of MBP intensity (D) in cauda equina sections from EAN rats. Scale bar, 50 μm. E, Representative toluidine blue staining images of cauda equine. Scale bar, 10 μm. F, Quantification of the percentage of myelinated axons in cauda equine. There are significantly more myelinated axons in animals treated with Cyclo-dPAKKR than vehicle controls. G, Quantification of the axonal density in cauda equina. Axonal density in EAN rats is expressed as a percentage of axonal density in health control rats. Axonal density in vehicle-treated animals was significantly reduced by almost 60–70% (30–40% of healthy control), whereas Cyclo-dPAKKR administration protected the axonal loss (∼60% of healthy control). H, Representative electron micrographs of myelinated axons in cauda equina. Scale bar, 2 μm. Panel a’ (a higher magnification image from panel a) shows macrophage-mediated demyelination, as evident by the last vestige of compact myelin being stripped from an axon by a macrophage filled with compact myelin debris. Panel b’ (a higher magnification image from panel b) shows the normal appearing myelin sheath penetrated with macrophages (arrows indicate myelin fragments). I, Representative immunohistochemical images of IBa1 (a marker for macrophages) in transvers sections of cauda equina of rats subjected to EAN at disease peak (day 17). Scale bar, 50 μm. J, Quantification of IBa1+ macrophages from (F) reveals that Cyclo-dPAKKR significantly reduced macrophage infiltration in injured nerves compared with vehicle controls.