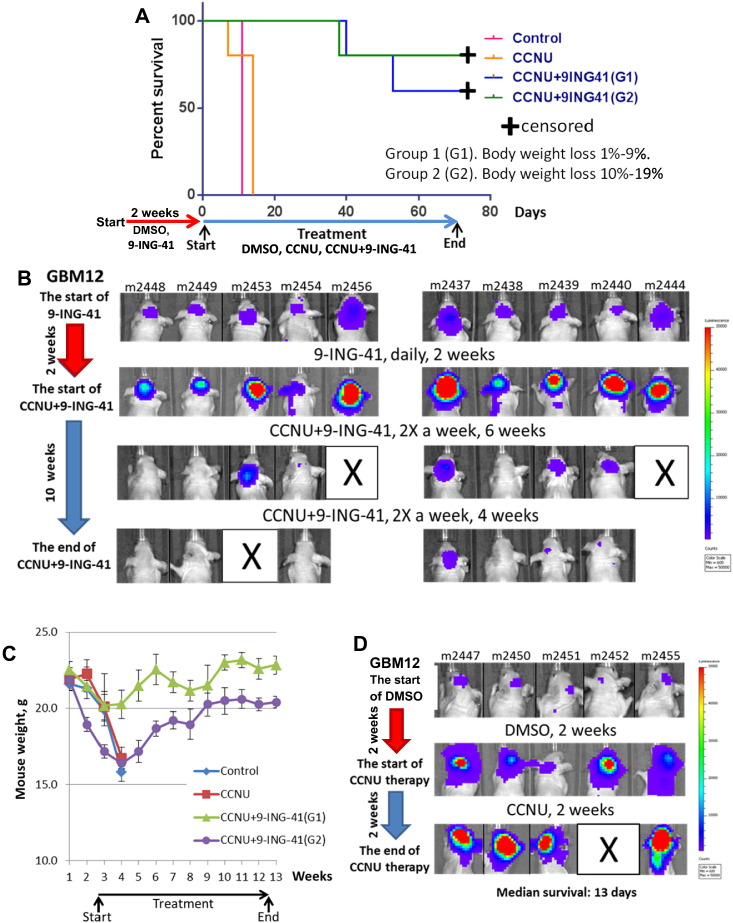
Figure 5.
Treatment with CCNU + 9-ING-41 leads to regression of intracranial GBM12 PDX tumors and recovery of cachectic mice. (A) Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of treated mice bearing intracranial human GBM12 PDX-Tom-Luc tumors. Mice were staged and randomized based on IVIS imaging. Mice were treated with vehicle control (DMSO; n = 10) or 40 mg/kg 9-ING-41 (n = 10) daily for 2 weeks as indicated by red arrow. Next, mice were treated two times a week with DMSO (n = 5), 5 mg/kg CCNU (n = 5), and CCNU + 9-ING-41 (n = 10) as indicated by blue arrow. The median survival (from the start of vehicle, CCNU and CCNU + 9-ING-41 treatment) in the vehicle control and CCNU was 11 and 13 days, respectively. Six of ten 9-ING-41 + CCNU–treated animals were intentionally euthanized (censored) for histological analysis of brain at day 66 despite being healthy and luciferase-signal free. The combination of CCNU and 9-ING-41 significantly prolonged survival of cachectic animals as compared to CCNU-treated group (P < .05). (B) Representative IVIS images of GBM12-bearing animals treated i.p. with combination of 5 mg/kg CCNU and 40 mg/kg 9-ING-41 twice a week as indicated. (C) Animal weight was measured weekly. Graph, mean animal weight; bars, SE. (D) Representative IVIS images of GBM12-bearing animals treated i.p. with 5 mg/kg CCNU twice a week.