Figure 2.
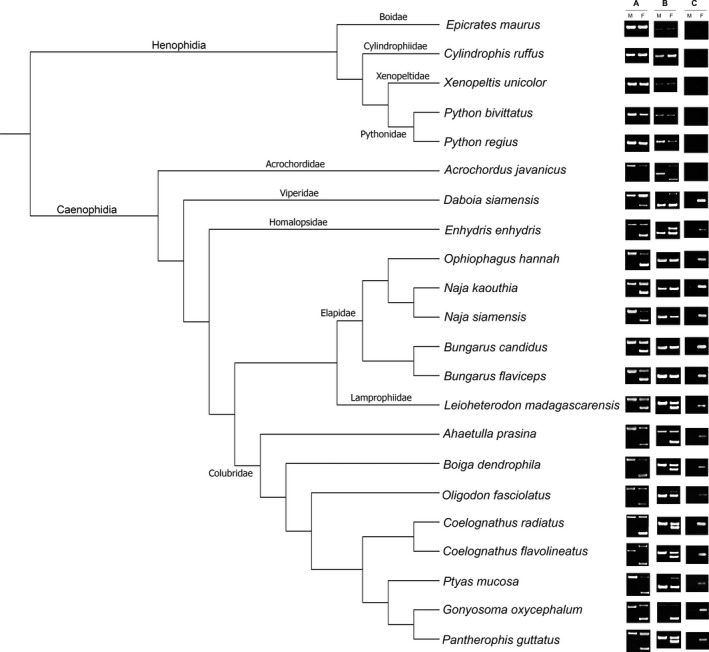
Phylogenetic relationships among sampled snake species illustrating the sex‐specific amplification of CTNNB1 and WAC genes using the primers: Eq‐CTNNB1‐11‐F1 and Eq‐CTNNB1‐13‐R; Eq‐WAC‐int9‐F and Eq‐WAC‐int9‐R; and CTNNB1W‐F and Eq‐CTNNB1‐13‐R. Phylogeny was partially derived from Vidal, Rage, Couloux, and Hedges (2009). Agarose gel electrophoresis of PCR products in males and females of twenty‐two snake species using three sexing markers: Eq‐CTNNB1‐11‐F1 and Eq‐CTNNB1‐13‐R (column A), Eq‐WAC‐int9‐F and Eq‐WAC‐int9‐R (column B), and CTNNB1W‐F and Eq‐CTNNB1‐13‐R (column C) are indicated at the right edge of the tree. M, male; F, female
