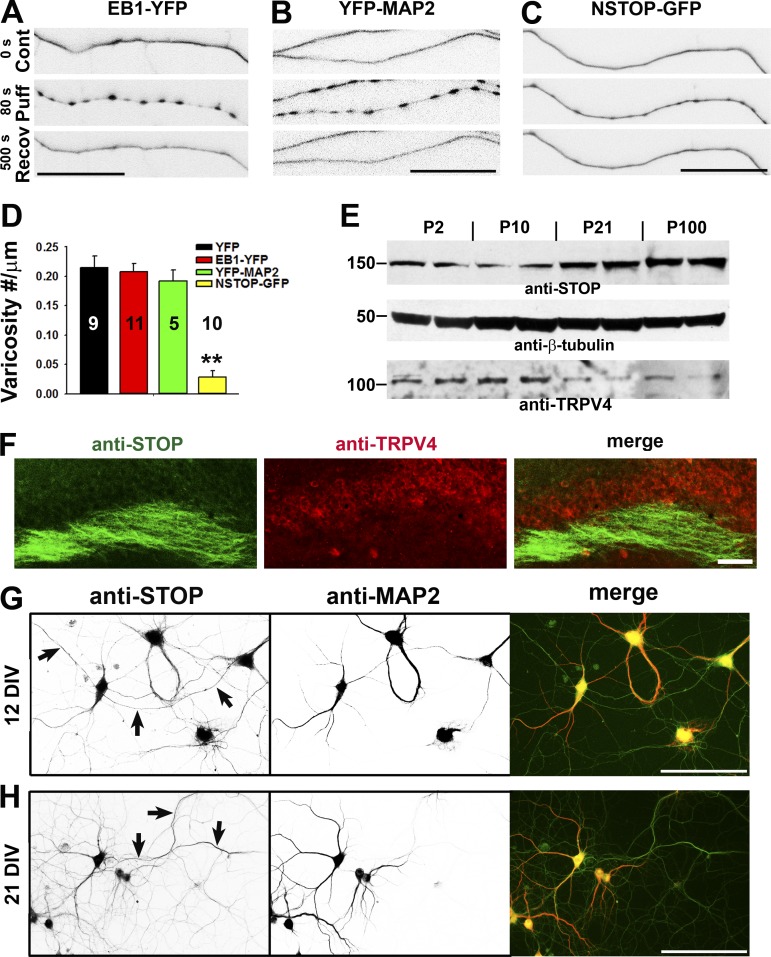
Figure 6.
The level of MT-binding protein NSTOP correlates with the resistance of puffing-induced varicosity formation. (A and B) Axons expressing different MT-binding proteins were puffed, and expressing EB1-YFP (A) or YFP-MAP2 (B) in axons did not change puffing-induced varicosity formation. (C) The axon expressing NSTOP-GFP became more resistant to puffing. (D) Summary of the effects of three MT-binding proteins on axonal varicosity formation. Error bars indicate means ± SEM. One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test: **, P < 0.01. (E) Expression levels of STOP and TRPV4 in the brain during development. Western blotting for STOP and TRPV4 from mouse brain lysate was performed, and β-tubulin was used as a control. Molecular masses are indicated in kilodaltons. (F) Costaining for endogenous STOP (green) and TRPV4 (red) in the hippocampal slice of an adult mouse. (G and H) Costaining for endogenous STOP (green in merged) and MAP2 (red in merged) was performed in cultured hippocampal neurons at 12 DIV (G) and 21 DIV (H). Arrows indicate MAP2-negative axons containing anti-STOP staining signals. Bars: (A–C) 25 µm; (F–H) 100 µm.