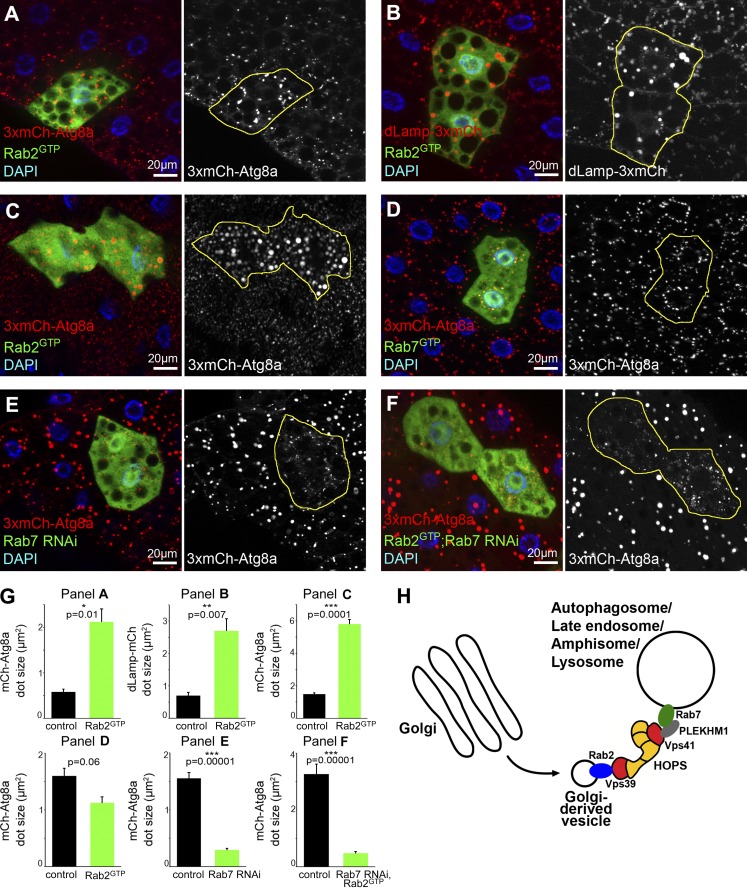
Figure 5.
Expression of Rab2GTP increases autolysosome size in starved Drosophila larvae. (A–C) Expression of active YFP-Rab2GTP leads to a striking increase in the size of 3xmCherry-Atg8a (A, fat cells; C, midgut cells) and dLamp-3xmCherry structures (B, fat cells), compared with surrounding control cells. Note that Rab-expressing cells coexpress free GFP to visualize cell outlines in these and all subsequent panels. (D) YFP-Rab7GTP expression does not affect 3xmCherry-Atg8a vesicle size. (E and F) Knockdown of Rab7 (E) in GFP+ cells causes accumulation of small faint autophagosomes and lack of bigger, brighter autolysosomes seen in neighboring control cells, based on 3xmCherry-Atg8a. Rab7 RNAi also prevents degradative autolysosome formation in cells expressing YFP-Rab2GTP (F). Quantification of data in A–F (G), n = 10 cells, error bars mark ± SEM. (H) A model of lysosomal fusions. We hypothesize that Rab2 is transported in Golgi-derived vesicles to fuse with Rab7-positive autophagosomes, late endosomes, amphisomes, and auto/endolysosomes. Rab2 promotes fusions until its release from these vesicles via GTP hydrolysis. In this scenario, Rab2 may directly bind to the Vps39 end of HOPS, whereas Rab7 may interact with Vps41 via adaptors such as PLEKHM1.