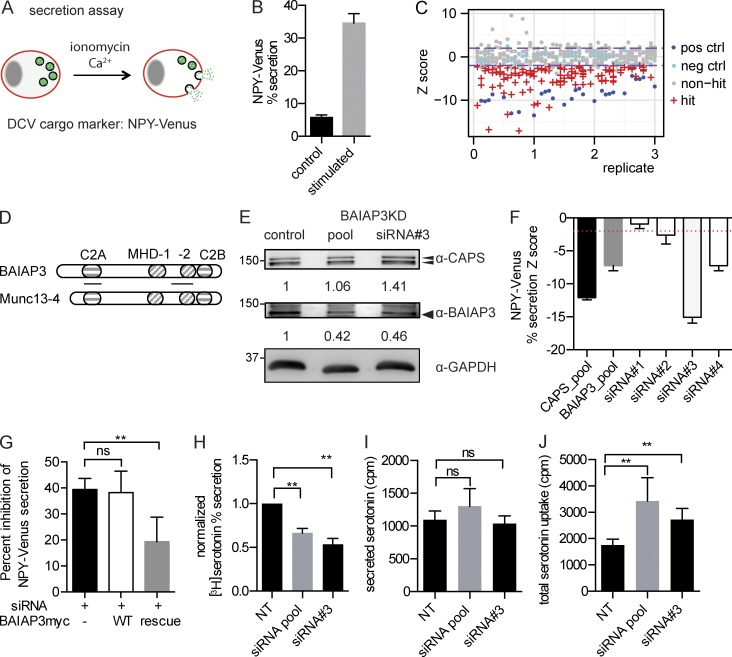
Figure 1.
BAIAP3 is required for acutely stimulated secretion. (A) Scheme of NPY-Venus secretion assay. (B) NPY-Venus percent secretion for 1.25-µM ionomycin stimulation or DMSO (control) treatment for 10 min in the presence of external 2.2 mM Ca2+. n = 48 and 45. (C) Triplicated siRNA screen of C2 domain–containing proteins. Each point corresponds to NPY-Venus percent secretion from 1 well after siRNA treatment. Positive control (pos ctrl; blue): CADPS siRNA; negative control (neg ctrl; cyan): a nontargeting siRNA; hits (red); non-hits (gray); purple lines: threshold for hit identification (z score = ±2). (D) Alignment of BAIAP3 with Munc13-4. Lines under BAIAP3 indicate esiRNA target regions. Other symbols show the indicated domains. (E) Expression of BAIAP3 in BON cells. The bands are quantified after normalizing to GAPDH. Molecular mass is shown in kilodaltons. (F) Validation of BAIAP3 knockdown effect on NPY-Venus percent secretion with individual siRNA duplexes. n = 5. The red dotted line indicates z score = −2. (G) Rescue of NPY-Venus secretion by siRNA-resistant BAIAP3. The effect of each treatment is represented as percent inhibition of NPY-Venus secretion. n = 5. Parallel studies indicated that ∼43% of the cells were transduced with siRNA-resistant BAIAP3 accounting for incomplete rescue. (H) Ca2+-induced [3H]serotonin percent secretion. Nontargeting (NT) siRNA is set as 1. n = 4. (I and J) Secreted and total uptake of [3H]serotonin (secreted + lysate). n = 4. See also Fig. S1. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. P-values were obtained by a two-tailed Student’s t test. **, P < 0.01.