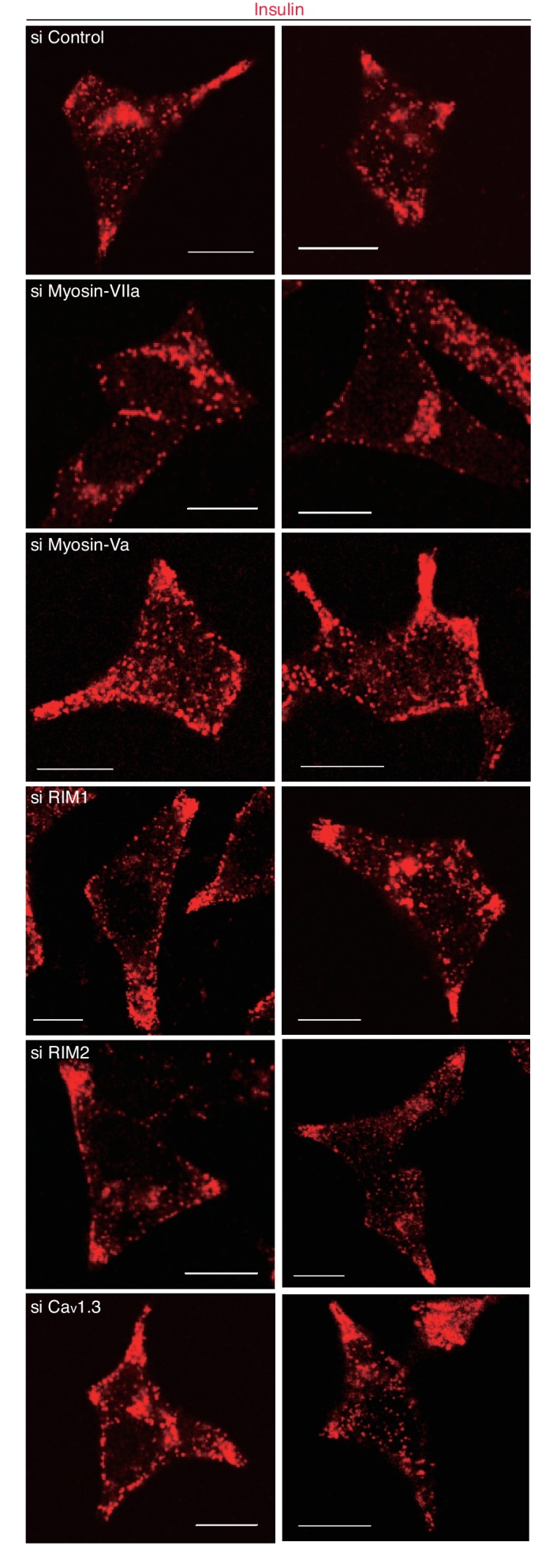
Figure 10. Myosin-VIIa clusters granules at cell corners.
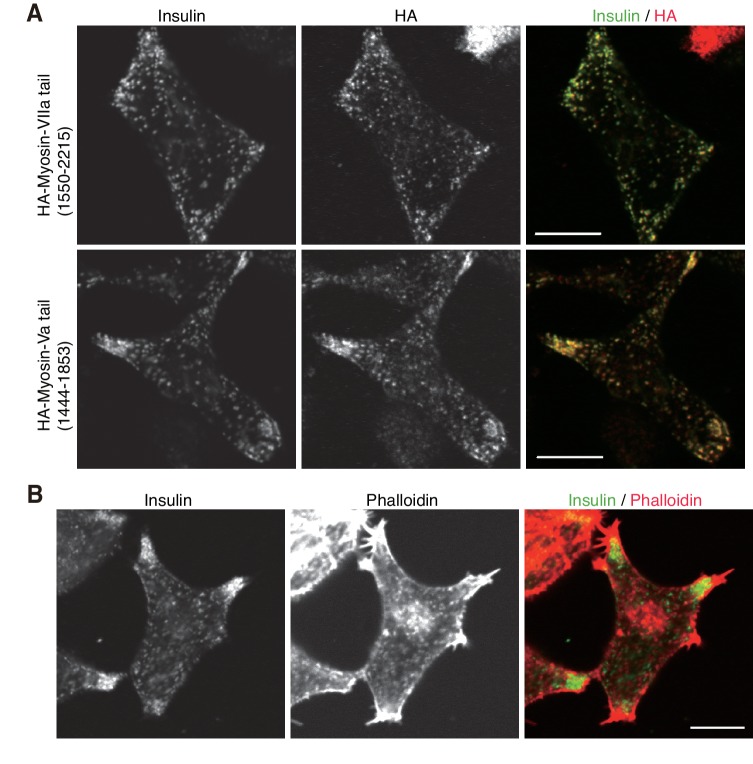
(A–C) INS-1 832–13 cells were transfected with control siRNA duplexes or siRNA duplexes against the indicated proteins (Figure 9B, Figure 10—figure supplement 1) and were subjected to insulin secretion assays (A) as described in Figure 7B, or to insulin immunostaining (B, C) to examine the peripheral accumulation of granules as described in Figure 6C–E. (D) INS-1 832/13 cells were coimmunostained with anti-insulin antibody and either with anti-myosin-Va or -VIIa antibody. Bars, 10 μm. All quantitative data are means ± SD (n = 4). *p values calculated using two-tailed unpaired t-test are as follows: (A) 0.00029 (si Myosin-VIIa), 0.01168 (si Myosin-Va), 0.01881 (si RIM1), 0.00688 (si RIM2), 0.00045 (si Cav1.3) vs si Control, and (B) 6.2 × 10−5 (si Myosin-VIIa) vs si Control.
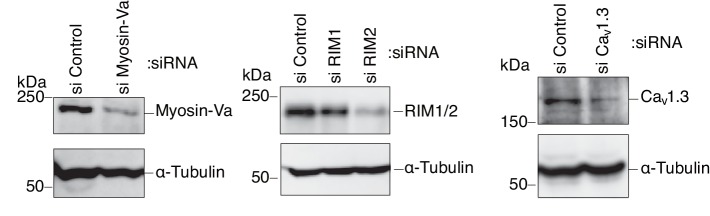
Figure 10—figure supplement 1. Silencing of myosin-Va, RIM, and Cav1.3 by siRNA.
Figure 10—figure supplement 2. More images of INS-1 832–13 cells treated with siRNA.