Figure 5.
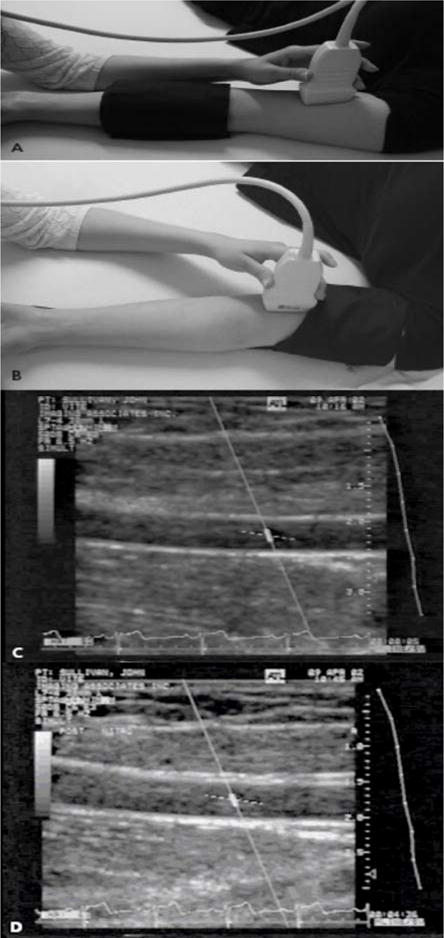
Assessment of FMD in the brachial artery. A 7.0-MHz or greater liner array transducer is used to image the brachial artery above the antecubital fossa in the longitudinal plane. A blood pressure cuff is employed to occlude the arterial blood flow and can be placed either at the forearm (a) or the upper arm level (b). Two-dimensional grayscale scans are taken, one at rest at rest, before the cuff inflation (c) and 1 minute after the cuff deflation that leads to arterial dilation (d). The percentage of the postocclusive artery diameter increase over the baseline represents the FMD. Figure adapted with permission from A. Veves (145).
