Fig. 1.
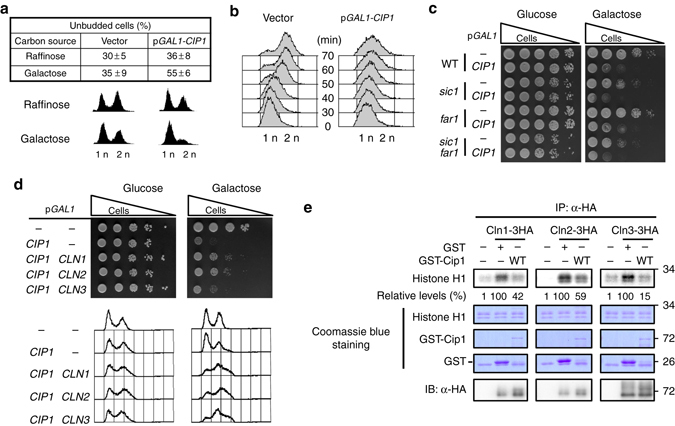
Overexpression of CIP1 causes cell cycle arrest at G1 through inhibition of all Cdk1–G1 cyclin complexes. a Strains bearing either the empty vector or GAL1-CIP1 plasmid were pre-grown in 2% raffinose medium and then added 2% galactose to induce for 9 h. The percentage of unbudded cells was scored. The values were given as mean ± s.d. (n = 3). The DNA content was shown below by FACS analysis. b Strains with the empty vector or GAL1-CIP1 plasmids were first arrested at G1 phase by α-factor in 2% raffinose culture. Cip1 was induced in the present of 2% galactose. The α-factor was subsequently removed from the cultures, and samples were collected at the indicated time points for flow cytometry analysis. c Isogenic wild-type (WT), far1, and sic1 strains harboring the empty vector or GAL1-CIP1 plasmid were spotted in 10-fold diluted equal number of yeast on 2% glucose and 2% galactose plates. d Strains bearing the LEU2 empty vector or GAL1-CIP1 plasmids were co-transformed with the URA3 empty vector, GAL1-CLN1, GAL1-CLN2, or GAL1-CLN3 plasmids. Cells were spotted in 10-fold diluted equal number of yeast on 2% glucose and 2% galactose plates. The FACS analysis of these strains is shown below. e The Cdk1-cyclins were immunoprecipitated from strains bearing the empty vector or plasmids with GAL1 driven 3HA tagged Cln1, Cln2, or Cln3 and incubated with recombinant Cip1. Histone H1 was used for the kinase substrate. The kinase activity was shown as the relative signals of 32P-labeled histone H1. The immune precipitates were probed with anti-HA antibody to detect the levels of purified cyclins. The uncropped Coomassie blue images are shown in Supplementary Fig. 11
