Fig. 8.
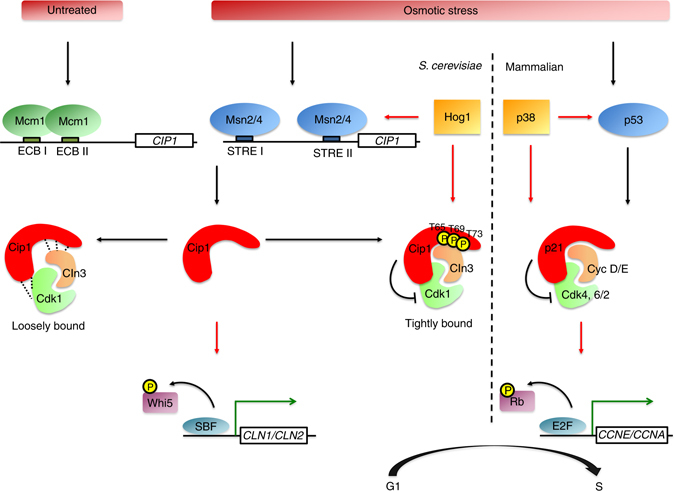
The Cip1-involved regulatory pathways of G1/S transition controlled by p38/Hog1 SAPKs in mammal/yeast upon osmotic stress. At M/G1 transition, Mcm1 binds at ECB element on CIP1 promoter and promotes the transcriptional expression of CIP1. Upon osmotic stress, active p38 and Hog1 SAPKs phosphorylate p53 and Msn2/4, respectively. In budding yeast, expression of Cip1 is induced by Msn2/4 and expressed Cip1 is phosphorylated at T65, T69, and T73 by Hog1. The phosphorylation of Cip1 strengthens the binding affinity with the Cdk1–Cln3 complex. The interaction between Cip1 and Cdk1–Cln3 complex inhibits the Cdk1–Cln3 kinase activity and prevents Cdk1–Cln3-complex-dependent Whi5 phosphorylation. Non-phosphorylated Whi5 binds to SBF, blocks G1/S genes transcription, and delays G1/S transition. In mammalian cells, the CDK inhibitor p21 is induced by activated p53 which leads to G1 arrest through inhibition of Cdk4, 6/2-cyclin D/E complexes
