Figure 1.
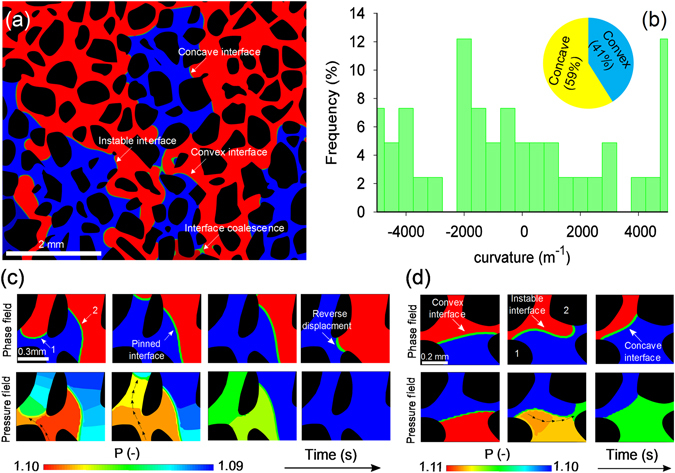
(a) The main interfacial features observed during immiscible two-phase flow in intermediate-wet porous media (θ = 60°) at 2.8 s. (b) Curvature distribution of interfaces shown in Fig. 1(a). (c) Dynamics of concave (labelled as “1”) and convex (labelled as “2”) interfaces during displacement in the porous medium with θ = 60°. Pinning of convex interface and reverse displacement mechanism as a result of co-existence of concave and convex interface is observed. (d) Interface instability in a single pore. In the phase distribution shown in Fig. 1(a,c,d), red, blue and green represents defending fluid, invading fluid and the fluid-fluid interface, respectively. The pressure field shown in Fig. 1(c–d) indicates the pressure values normalized with respect to the outlet pressure. The direction of injection in all images is from bottom to top.
