Figure 1.
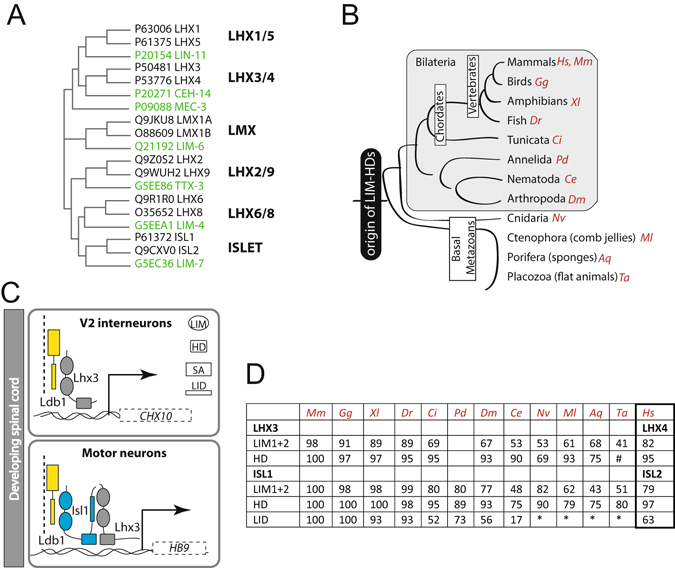
Islet- and LHX3-family LIM-HD proteins and interactors. (A) Simple phylogenetic tree diagram of LIM-HD proteins from mouse (black) and C. elegans (green) illustrating the LIM-HD families; Uniprot accession codes are provided. Branches and relationships are derived from analysis of these proteins using CLUSTAL OMEGA and CLUSTAL PHYLOGENY. Distances are not to scale. (B) Schematic of evolutionary relationships in metazoans. Hs – Homo sapiens; Ms – Mus musculus; Gg – Gallus gallus, Xl – Xenopus laevis, Dr – Danio rerio, Ci – Ciona intestinalis, Pd - Platynereis dumerilii, Ce -Caenorhabditis elegans, Dm – Drosophila melanogasta, Nv - Nematostella vectensis, Ml - Mnemiopsis leidyi, Aq- Amphimedon queenslandica, Ta - Trichoplax adhaerens. The branchpoints between some basal metazoans are controversial70, 71 and not indicated here. (C) Distinct transcriptional complexes drive different transcription programs in adjacent cell types in the developing ventral spinal cord in vertebrates. (D) Sequence identity (% compared to Hs proteins) between domains in metazoan LHX3 and ISL1 proteins. No domain identified (*), substantially truncated domain identified (#). No PdLHX3 gene was found.
