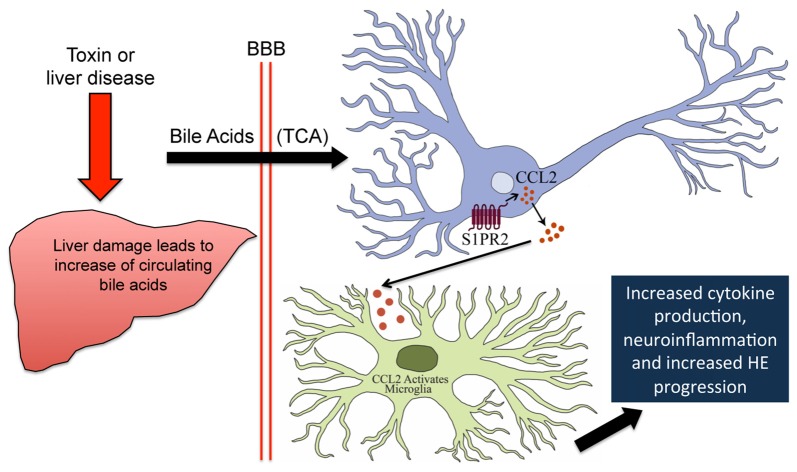
Figure 7.
Working model of S1PR2-mediated neuroinflammation during AOM-induced HE. AOM-induced liver failure disrupts the enterohepatic circulation and causes hepatocyte death leading to an increase of circulating bile acids including TCA. TCA crosses the leaky blood brain barrier and binds S1PR2 in neurons. This leads to increased expression and secretion of CCL2 from neurons, which binds receptors on microglia leading to their activation. This ultimately results in increased proinflammatory cytokine expression and worse HE outcomes.